[ad_1]
The quantity of birthdays you’ve had—better acknowledged as your chronological age—now appears to be considerably less significant in evaluating your wellbeing than at any time just before. A new examine exhibits that bodily organs get “older” at extraordinarily diverse premiums, and every one’s organic age can be at odds with a person’s age on paper.
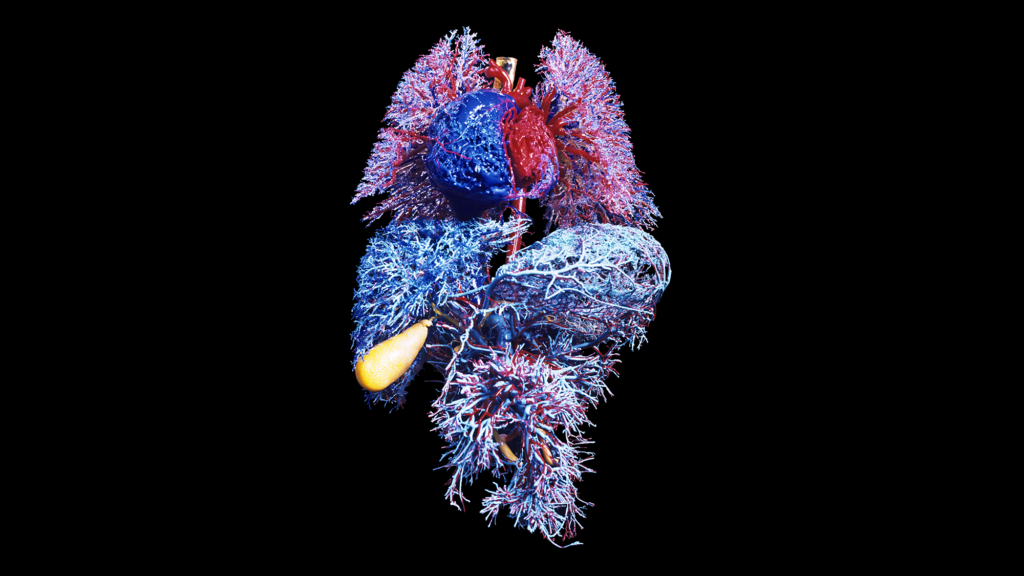
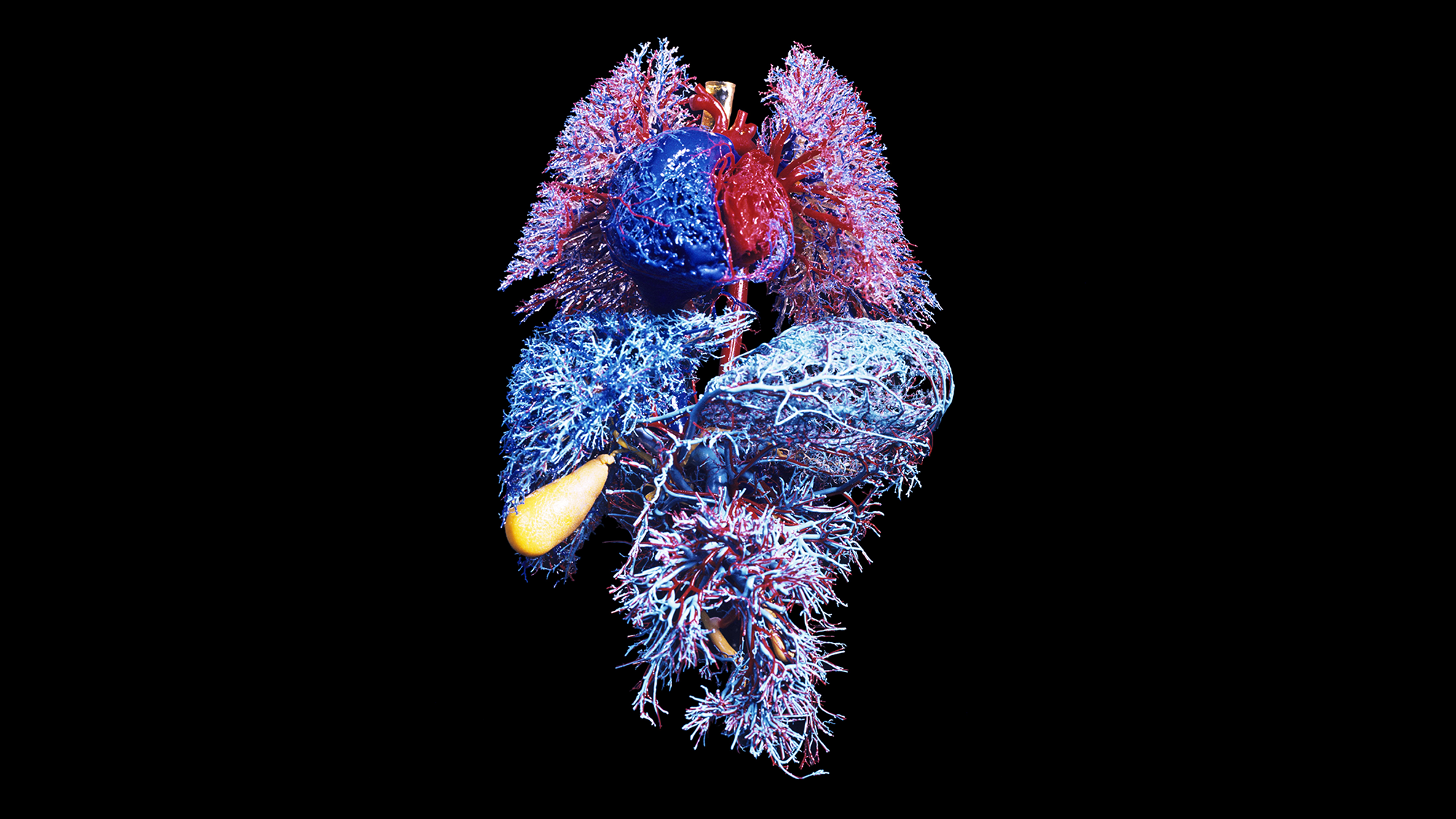
The new investigate, released on Wednesday in Character, recognized about just one in five wholesome adults older than 50 several years old as an “extreme ager”—a human being with at the very least a person organ aging at a highly accelerated amount, in comparison with a cohort of their peers. A person in 60 grownups had two or far more organs that had been ageing promptly. The review team calculated proteins similar to organs, including the brain, coronary heart, immune tissue and kidneys. The scientists hope their conclusions will guide to a potential blood exam that can pinpoint speedily growing older organs, allowing health professionals goal them for treatment prior to ailment signs and symptoms start.
The crew sampled the blood of extra than 5,500 people, all with no lively condition or clinically abnormal biomarkers, to seem for proteins that originated from distinct organs. The scientists had been equipped to figure out exactly where people proteins arrived from by measuring their gene exercise: when genes for a protein were expressed four times extra in one particular organ, that specified its origin. Up coming the workforce calculated the concentrations of hundreds of proteins in a drop of blood and identified that practically 900 of them—about 18 % of the proteins measured—tended to be distinct to a single organ. When people proteins diversified from the envisioned concentration for a particular chronological age, that indicated accelerated getting old in the corresponding organ.
“We could say with sensible certainty that [a particular protein] possible comes from the mind and in some way ends up in the blood,” clarifies Tony Wyss-Coray, a professor of neurology at Stanford College and co-creator of the new study. If that protein concentration modifications in the blood, “it will have to also likely modify in the brain—and [that] tells us a little something about how the brain ages,” Wyss-Coray states.
By evaluating review participants’ organ-certain proteins, the researchers had been able to estimate an age gap—the change amongst an organ’s organic age and its chronological age. Based on the organ included, members identified to have at minimum a person with accelerated growing old had an amplified illness and mortality risk in excess of the next 15 many years. For instance, those people whose coronary heart was “older” than common had far more than 2 times the danger of heart failure than people with a generally getting older coronary heart. Growing older in the heart was also a robust predictor of heart assault. In the same way, those people with a immediately aging brain have been much more possible to encounter cognitive drop. Accelerated aging in the mind and vascular procedure predicted the development of Alzheimer’s sickness just as strongly as plasma pTau-181—the latest clinical blood biomarker for the condition. Extreme aging in the kidneys was a strong predictor of hypertension and diabetic issues.
Paul Shiels, a professor of mobile gerontology at the College of Glasgow, who was not concerned in the new investigation, suggests the examine was properly run with sizable cohorts. But the age selection of the individuals included was “a tiny narrow,” he says. “It only seemed at more mature persons, and it was not agent of a full daily life system.”
The measurement of biological ageing is an evolving science. “Epigenetic clocks,” a foremost tactic pioneered by Steve Horvath of the biotechnology research start off-up Altos Labs, search at DNA adjustments to determine tissue age more correctly than other current biological age estimators. When people age, the physique commences to accumulate DNA signatures that can suggest how old a cell or organ is this will allow estimates of age. But epigenetic clocks estimate the age of the full organism as an alternative of an organ-certain age, Wyss-Coray says.
Other earlier operate by Michael Snyder, a genomicist at Stanford College, has developed “ageotypes” that categorize ageing into four distinctive pathways: by way of the kidneys, liver, immune procedure and basic fat burning capacity. Wyss-Coray and his colleagues’ operate expands these getting old pathways to far more organs and system systems.
Wyss-Coray anticipates this investigation could guide to a basic blood examination that could guideline prognostic work—in other words, a take a look at that could assist foretell potential health issues. “You could commence to do interventions in advance of that individual develops condition,” he claims, “and likely reverse this accelerating ageing or slow it down.”
This exploration is element of the growing area of personalized diagnostics, which is based on the thought that many biological indicators of organ well being can assist clinicians focus on remedy. Blood measurements have ordinarily been utilized to identify ailment in the entire body, with clinicians building a analysis only immediately after a individual crosses the threshold of a sure established indicator. But as protein markers turn into more sensitive, “you can actually detect a thing irregular prior to you have clinical manifestations,” Wyss-Coray claims. He and his colleagues built-in this investigation into a recently submitted patent tied to their begin-up firm Teal Omics, which focuses on precision drugs by way of biomarker testing.
Some corporations, mainly primarily based in California, presently provide blood, urine or saliva testing that purports to establish one’s general biological age. The momentum of industrial epigenetic screening is a “gold rush,” Shiels suggests. “There is a degree of oversell on what [the tests] can do.”
A solitary organ doesn’t tell the whole tale of getting old simply because deterioration processes are interconnected and influence an whole organism. “We fully grasp a lot about the growing older procedure on sort of a micro stage,” Shiels says. “But a great deal of the elements that travel age-connected organ dysfunction are environmental. So it is life style, pollution, what you try to eat, microbes in your intestine.”
In accordance to Wyss-Coray, every organ is essential to general wellness. He likens the human body to a automobile: “If 1 section does not operate effectively, the other areas commence to suffer,” he suggests. “If you maintain specified elements, you can prolong the lifestyle span of the auto.”
[ad_2]
Source connection