[ad_1]
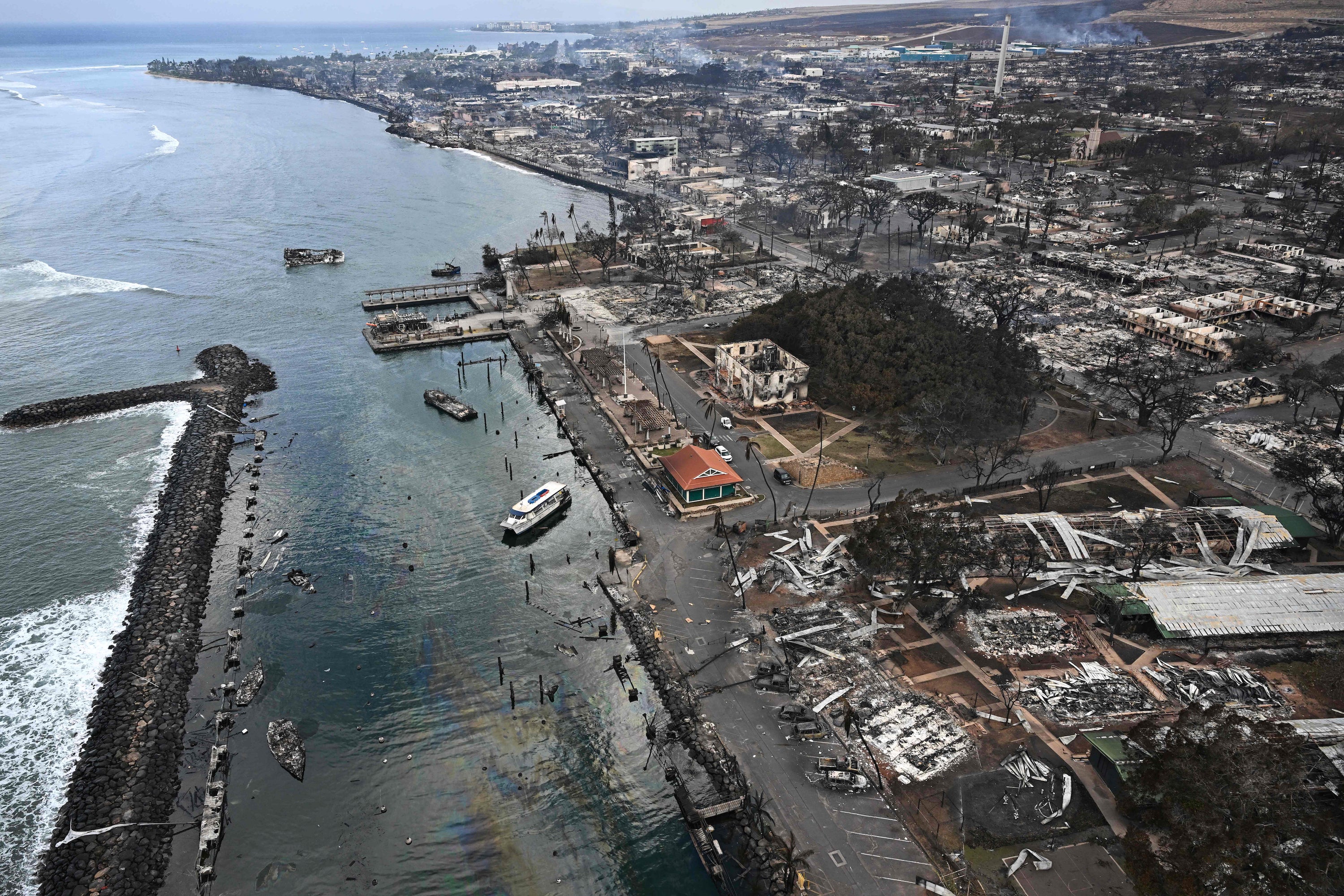

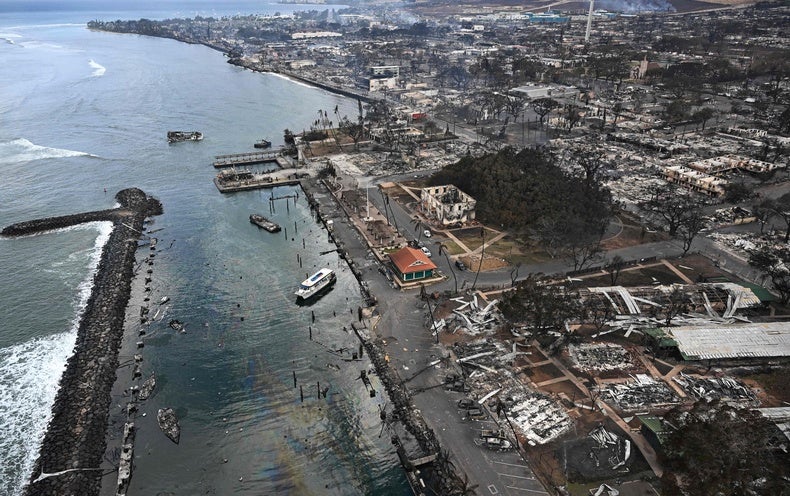
Maui is reeling from wildfires that devastated the Hawaiian island past week. They have taken at least 99 lives and brought about a lot more than US$5.52 billion pounds of harm. But did the fires consider scientists by surprise and how can Hawaii guard against these types of disasters in future?
Wildfires are not new to Hawaii. While outsiders are inclined to consider of the Pacific archipelago as a put of lush tropical vegetation, just about every island has a drier leeward facet that is sheltered from the wind — this is where tourism tends to be concentrated, since of the sunny weather conditions. Lahaina, where by the most lethal hearth broke out on 8 August, usually means ‘cruel sun’ in Hawaiian this element of Maui has generally been hot and dry.
What’s far more, Hawaiian fires are obtaining even worse and far more recurrent. “We’ve been looking at a really steady raise, and in the very last handful of decades, an exponential maximize in the amount of location that burns in Hawaii each individual year,” suggests climatologist Abby Frazier at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts.
A 2021 report by Maui County observed that “the quantity of incidents from a blend of wild/brush/forest fires appears to be raising, and that this enhance poses an increased threat to citizens, properties and sacred sites”.
Fire’s will cause
The three most important components of a wildfire are gas, dryness and an ignition supply. Hawaii’s crucial gas is grass, which proliferated in former agricultural regions as the overall economy shifted from ranching and sugar and pineapple cultivation to tourism. When dry grasses burn up, they can have hearth to forested locations, which are likely to turn into grasslands following the fireplace, in a self-perpetuating cycle.
The dryness demanded for the wildfires came from droughts, which are “lasting more time and finding more severe” throughout Hawaii, according to Frazier, who researched how rainfall patterns have transformed in the islands more than the past century. Temperatures have enhanced, owing to weather alter, which dries out vegetation quicker. Irrespective of whether local weather change is also creating a reduction in rainfall is more challenging to verify, Frazier states. The issues stems in part from various complicated periodic weather conditions patterns that dominate the Pacific’s organic climate, this kind of as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.
The Pacific knowledgeable a La Niña stage of the ENSO from the stop of 2022 to early 2023, which meant a very damp soaked season. Maui observed rainfall that was 90–120% of usual, main to sturdy grass expansion. In June, El Niño — which commonly provides hotter, drier climate — returned.
El Niño does not constantly deliver drought in the course of Hawaii’s dry time, which runs among May well and October. But forecasters at the US Countrywide Atmospheric and Oceanic Administration ended up predicting underneath normal precipitation and drought for Hawaii — and for the leeward side of Maui in particular — as early as May possibly.
The ignition source for the fires on the island past 7 days is however not identified, whilst one particular chance is sparks from downed electric power traces or other electrical units. What is very clear is that higher winds from Hurricane Dora, just 500 miles offshore, would have served change localized fires into a fast-going inferno. As early as 4 August, the US Countrywide Climate Assistance was noting that Dora’s winds, blended with drought, would generate risky fire-weather conditions problems. On 7 August, the company issued a Pink Flag Warning for fire danger for the leeward areas of all Hawaiian Islands.
Controlling hearth in Hawaii
What could be done to guard against catastrophe in foreseeable future? Among other steps, the 2021 Maui County report advised that the island emphasize avoidance of ignition by means of community education and learning and tackling the grasses that provide as gasoline for several Hawaiian fires. It called for an “aggressive prepare to replace these dangerous gasoline resources with indigenous vegetation to lessen flamable gas when raising water retention”.
The flammable grasses in issue — including Cenchrus clandestinus (kikuyu grass), Cenchrus setaceus (fountain grass), Melinus minutiflora (molasses grass) and Megathyrsus maximus (guinea grass) — were launched close to the flip of the twentieth century as forage or ornamental crops. But indigenous Hawaiian dryland plants are not essentially extra hearth resistant, says Katie Kamelamela, an ethnoecologist at Arizona Condition University in Tempe. What matters is how a great deal dry fuel is on the land, and how it is arranged. Grazing can decrease gas loads. Bare areas, wet vegetation in the form of active farms, or even fish ponds can aid quit or gradual fires.
Kamelamela, who is Native Hawaiian, says that regardless of whether the plants in an area are indigenous or introduced is considerably less crucial than how meticulously land is cared for. In the earlier, persons who collected means from a forest would also tidy it up, taking away undergrowth or even replanting critical plants. But this kind of labour-intense traditional work is challenging to in shape into a busy modern-day lifestyle. “Most people today in Hawaii have two to 3 work and are just trying to choose their children to soccer exercise,” she claims.
Fascination is growing among the numerous Native Hawaiians and Hawaii inhabitants in reinvesting in classic kinds of agriculture and aquaculture. Teams these as Ao‘ao O Nā Loko I‘a O Maui (the Maui Fishpond Affiliation) and Kipahulu Ohana are striving to revitalize traditional food stuff creation, which would build a landscape that is a lot a lot less flammable than the untended grasslands that at this time go over 24% of the state’s overall land area. A 2019 examine found that Hawaii’s conventional agroecosystems could aid just about all of the islands’ existing inhabitants.
Kamelamela says that changing the way that Hawaii manages its lands could create a further relationship amongst folks and place. “That’s why these fires begun: because no a single experienced a marriage to these areas.”
Climatologists and meteorologists also want the assortment and dissemination of Hawaii’s local climate data to arrive into line with the contiguous United States. There is no everyday or regular monthly facts for soil dampness or prospective evapotranspiration accessible for Hawaii, and the point out is not incorporated in many of the scientific items issued by the US federal authorities, such as the Crop Humidity Index. But the University of Hawaii has high-resolution grid data on temperature, rainfall and other variables, says Frazier.
Hawaii is the only condition without a committed climate division in just the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Adminisatration (NOAA) — one thing Frazier and a group of colleagues are hoping to adjust. “Much better integration with NOAA and extra details products and solutions accessible would allow us to far better understand hazard threats in authentic time,” she claims.
This post is reproduced with authorization and was initially published on August 14, 2023.
[ad_2]
Resource hyperlink