[ad_1]
Dreams have fascinated folks for millennia, still we struggle to comprehend their intent. Some theories propose desires assist us deal with thoughts, address issues or manage concealed desires. Other individuals postulate that they thoroughly clean up mind waste, make recollections stronger or deduce the which means of random brain activity. A extra latest principle suggests nighttime goals safeguard visible parts of the brain from getting co-opted throughout slumber by other sensory capabilities, such as hearing or contact.
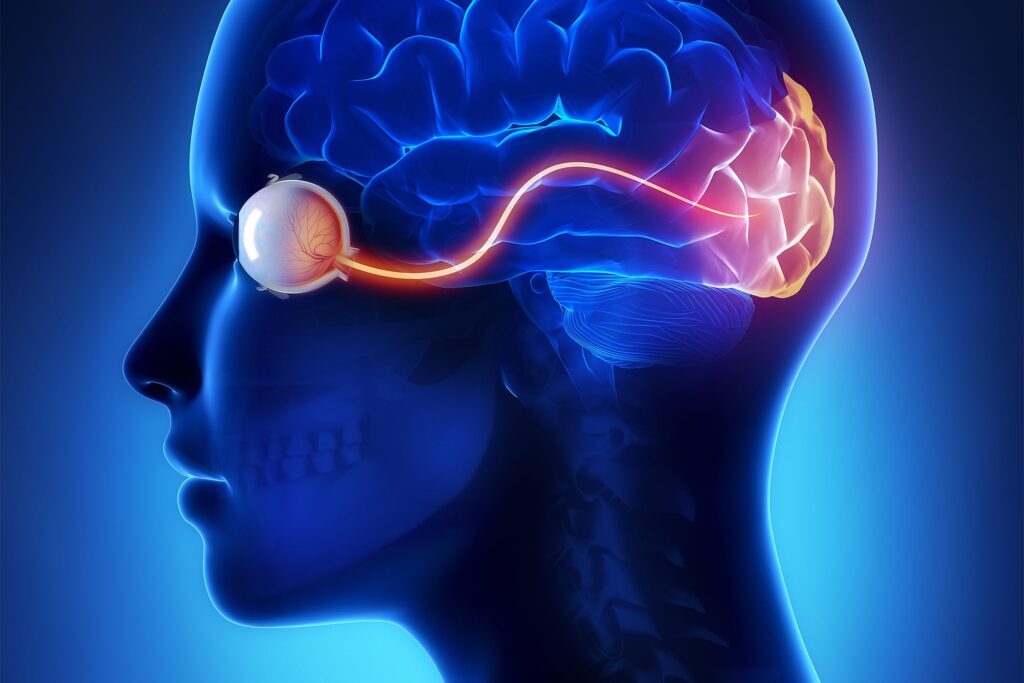
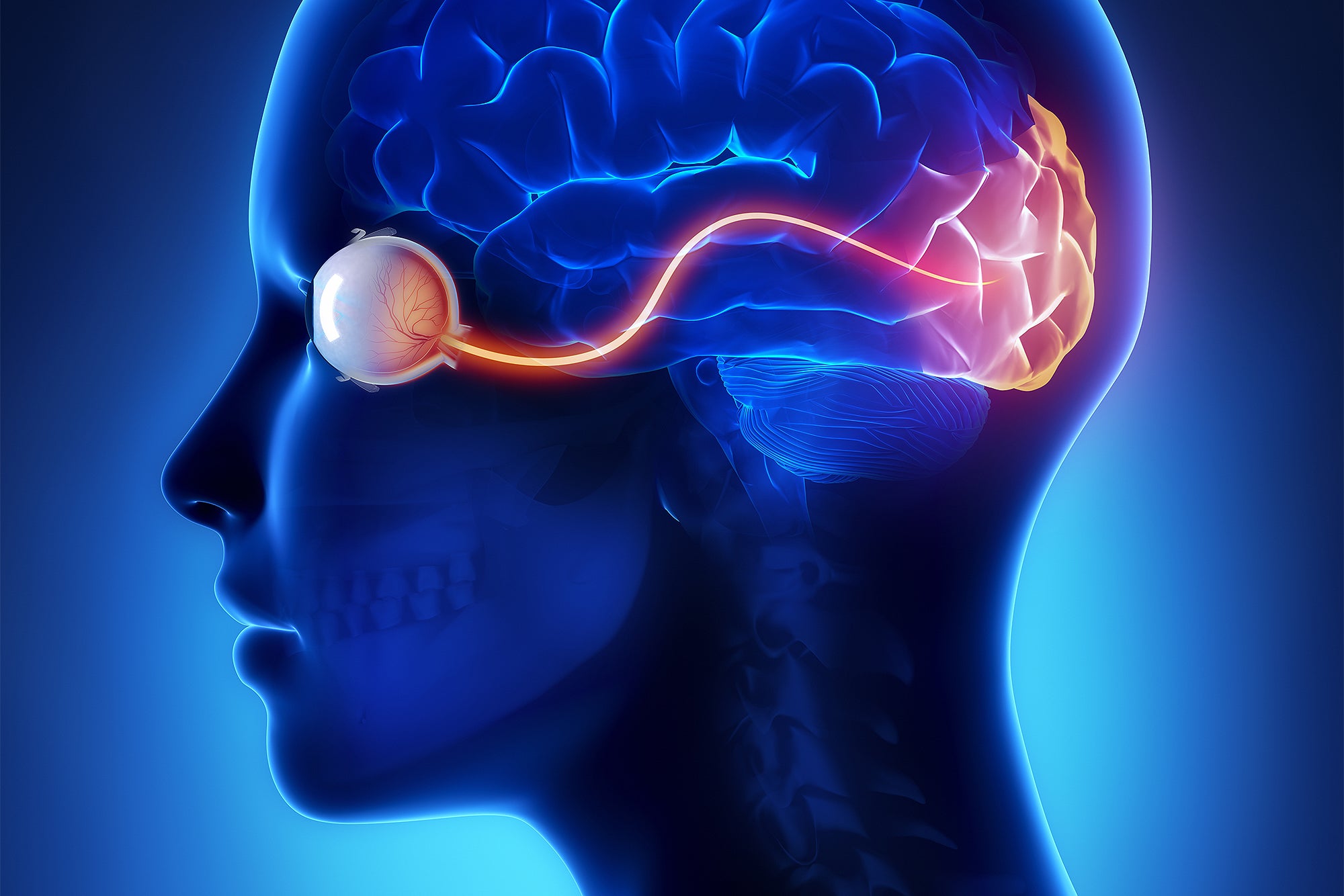
David Eagleman, a neuroscientist at Stanford University, has proposed the thought that dreaming is essential to safeguard the visual cortex—the portion of the brain liable for processing vision. Eagleman’s theory takes into account that the human mind is extremely adaptive, with sure places able to get on new responsibilities, an capacity referred to as neuroplasticity. He argues that neurons contend for survival. The mind, Eagleman clarifies, distributes its means by “implementing a do-or-die competition” for brain territory in which sensory places “gain or shed neural territory when inputs sluggish, halt or shift.” Encounters over a life span reshape the map of the mind. “Just like neighboring nations, neurons stake out their territory and chronically defend them,” he suggests.
Eagleman points to little ones who have had 50 % their mind removed since of extreme health and fitness troubles and then regain regular purpose. The remaining brain reorganizes by itself and usually takes about the roles of the missing sections. In the same way, individuals who reduce sight or hearing present heightened sensitivity in the remaining senses simply because the location of the brain typically utilized by the dropped perception is taken around by other senses.
Reorganization can materialize speedy. Reports posted in 2007 and 2008 by Lotfi Merabet of Harvard Medical University and his colleagues showed just how quickly this takeover can materialize. The 2008 review, in which subjects were blindfolded, disclosed that the seizing of an idle region by other senses commences in as minimal as 90 minutes. And other scientific tests identified that this can occur inside of 45 minutes.
When we sleep, we can odor, hear and sense, but visual information is absent—except in the course of REM slumber. About 90 minutes soon after drifting off to sleep, you enter REM. It commences when neurons in your brain stem, the stalklike part at the bottom of the organ, signal the commencing of two crucial jobs. Action of these neurons, for one, paralyze main muscle mass, avoiding the sleeper from acting out what is taking place in the desire. Also, these brain cells mail messages right to the visible cortex, which initiates the dreaming procedure.
Why does REM adhere to that timetable? It conforms to when the visual cortex requires to begin defending its territory, Eagleman argues. Scans of dreaming people today show most of the brain action linked with REM is within just the visible cortex. Dreams are the brain’s way of combating takeover from other senses, in accordance to Eagleman, and REM activation prompts internally generated action in the visual cortex as a implies to safeguard its territory. As lengthy as the neurons in the visible cortex are actively accomplishing their customary job—in this case, making visible imagery—they will not be commandeered by close by neurons that approach other sensory info.
Eagleman argues that the far more plastic the brain, the additional REM slumber is needed to mount a protection. For toddlers to produce thoroughly, they need to slumber a lot, paying out almost 50 per cent of their time in REM rest. But as men and women age, their brain gets fewer versatile. (Assume of how effortlessly small children find out languages, compared with grown ups.) At the very same time, grown ups commit a lot less time in REM snooze.
The correlation in between adaptability and REM appears to maintain across species. According to Eagleman, “Mother Mother nature drops human brains into the environment half-baked and allows knowledge choose around and shape them.” He argues the significantly less hardwired a species’ brain is at delivery, the a lot more capacity it has to adapt and find out from expertise. But this has its disadvantages. For example, fawns and calves are capable to stroll within several hours of start due to the fact the conduct is hardwired. Human toddlers, with their a lot more adaptable brains, demand drastically more REM rest than animals born with additional hardwired brains.
Some researchers—in unique, desire researchers—disagree with Eagleman’s speculation. Just one example that raises doubts is the truth that the blind mole rat does not see and continue to experiences REM snooze. Yet some evolutionary variations are vestigial remnants of features that have been helpful in the previous but have come to be significantly less significant as animals have advanced. So potentially there was no stress for blind mole rats to eliminate REM exercise as they progressed without having eyesight.
Antonio Zadra, a dream researcher at the University of Montreal, claims Eagleman’s principle “has very little to do with precise dreaming and clarifies practically nothing about dreams for each se, as opposed to REM sleep.” He asserts the theory “is, for me and many some others who actually get the job done in the area, foolish and overly reductionistic and simplistic.”
Deirdre Leigh Barrett, a psychologist at Harvard University, former president of the Global Affiliation for the Examine of Dreams and creator of The Committee of Rest, even so, is much more ready to take into account Eagleman’s hypothesis. “It’s very convincing that you can find a correlation amongst smarter animals and extra elaborate brains,” she says. As far as dreams defending mind true estate, “I have a very little more difficulties with the visual argument, but it’s intriguing.”
Eagleman suggests that his theory can accommodate other explanations for dreams and that REM rest might provide lots of applications in addition to defending the visible cortex. Feel of dreaming like a laptop screen saver that is set to go off each 90 minutes—except that instead of guarding towards frozen photographs, desires prevent the visible cortex from being usurped by other features. These visible hallucinations in the night time might enable us see during the day.
[ad_2]
Supply backlink