[ad_1]
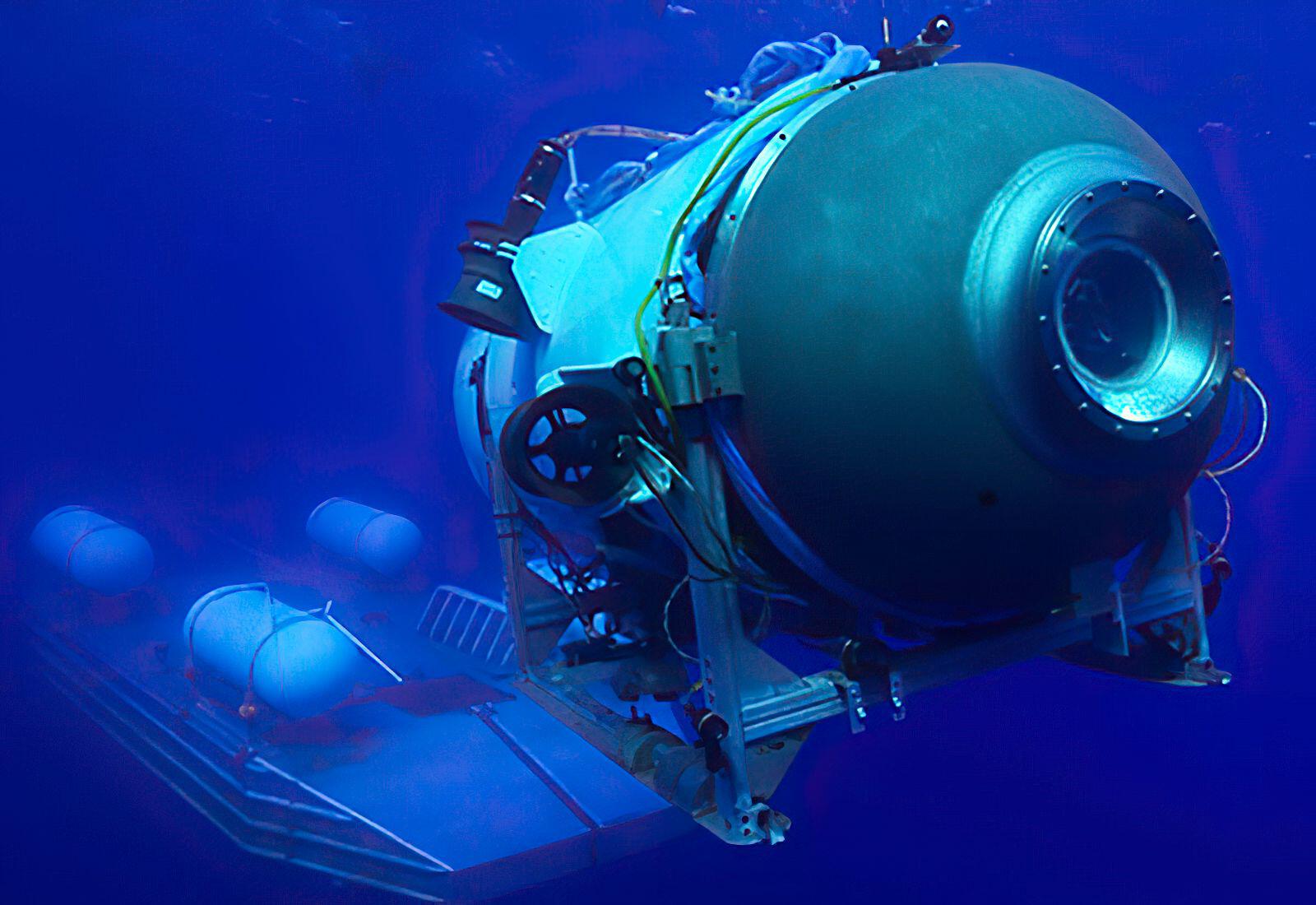
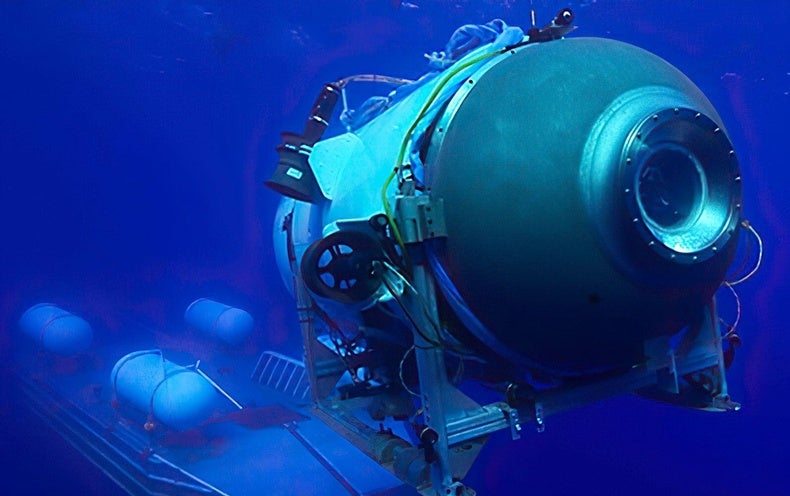
The oxygen provide of the missing Titan submersible is expected to operate out Thursday all around 6 a.m. EST (10 a.m. GMT).
A frantic look for carries on for the Titan and its 5 occupants, with sonar buoys getting recorded “banging” noises in the search place on Tuesday and Wednesday.
With the vessel’s destiny nonetheless to be determined, the basic public is inquiring thoughts about the protection of such touristic endeavors.
The context
The context in which the Titan has disappeared is disturbing. Reviews have come out detailing court files from a 2018 case that exhibit OceanGate, the company responsible for the Titan, fired worker David Lochridge immediately after he expressed worries about the submersible’s security.
Lochridge disagreed with OceanGate about the most effective way to show the asset’s seaworthiness, and objected to OceanGate’s decision to accomplish dives without the need of prior “non-destructive testing” to the vessel’s hull to verify its integrity.
Also in 2018, a letter despatched to OceanGate by the Manned Underwater Autos Committee of the Marine Technologies Modern society, signed by 38 specialists, expressed reservations about the submersible’s protection. They stated the “[…] experimental technique adopted by OceanGate could outcome in damaging results (from minor to catastrophic) that would have severe outcomes for absolutely everyone in the industry”.
As we can see from these exchanges, the engineering and regulation of deep-sea submersibles remains fairly uncharted territory. And given that the Titan operates in intercontinental waters, it is technically cost-free from governance by any solitary nation’s laws.
In this scenario, most submersible designers would elect to have a classification society certify the vessel’s style. OceanGate made the aware decision to refuse to do this for the Titan.
Seaworthiness of submersibles
When we discuss about the “seaworthiness” of a marine vessel, we are basically asking if it is suit for goal, harmless to operate, and compliant with the security of the surroundings.
For the Titan, health for purpose could be summarised by the skill to securely launch from a mothership on the water’s surface area, operate autonomously down to 4,000m (the approximate depth of the Titanic shipwreck), and resurface for restoration by the mothership following a dive of a few hours.
Security to function would imply no products is harmed and no travellers are vulnerable to injury (or even worse) even though onboard. And defense of surroundings suggests the submersible would not have any considerable effect on its environment, such as by pollution or disturbing the ecosystem.
Nevertheless, this is the blue-sky state of affairs. Deep-sea submersibles operate in a hostile setting, and items can go completely wrong.
Stress resistance
Submersibles and submarines are shaped the way they are since spheres and cylinders are geometrically additional resistant to crushing pressures.
As an alternative of operating in a breathable atmosphere of 1 bar, the Titan would have to withstand 370 bars of strain in seawater at the depth of the Titanic. Any defect in the hull could end result in instantaneous implosion.
So what is the threshold under which an “out-of-circularity” geometry becomes a defect?
Industries utilizing underwater vessels at depths of a number of hundred metres will normally use metal hulls, which ordinarily have an out-of-circularity threshold underneath .5% of the vessel’s diameter. Would that criterion be protected plenty of for the pressure hull of the Titan at 4,000m?
The Titan is built of a composite carbon fibre-titanium hull. It is really difficult to layout and structurally assess these materials, in comparison to metallic material only. A person can believe this is why OceanGate equipped the Titan with a “real-time hull overall health monitoring system”.
It is unclear if the process truly steps the stresses with strain gauges in the hull, or if it is (as Lochridge warned) an acoustic evaluation that would only notify people today about imminent difficulties “often milliseconds ahead of an implosion”.
Protection for force hull integrity involves analysing numerous failure modes, in advance of analyzing a basic safety coefficient for each individual mode, based on the deep diving depth aimed at.
Soon after the layout is confirmed (by way of calculations), authentic-earth validation ought to take place in two methods.
Non-harmful testing should really be accomplished on the created stress hull, to check out the preciseness of its geometry and any out-of-circularity factors.
Then, real dives (preferably unmanned) ought to be carried out at progressively escalating depths, with anxiety gauges utilised to evaluate true values against predictions. We don’t know no matter if the Titan underwent these assessments.
Again-ups and redundancy
In designing the useful architecture and selecting devices, a designer would think about a quantity of “what if” situations to recuperate from:
- 
- what if primary electrical power resources are unsuccessful?
- what if my computer crashes and the pilot loses command?
- what if my most important interaction system fails?
- how can the submersible signal to the mothership there is a issue?




These scenarios commit the naval architects to be certain what is named a safety SFAIRP (so much as is reasonably practicable). This requires not only mitigating the penalties of an accident, but also preventing it from taking place.
In simple conditions, it implies having:
- 
- a reserve of oxygen (this kind of as when waiting around for a rescue occasion)
- trusted primary electrical power sources and back-up systems
- one more energy resource (these as hydraulic) in circumstance of power decline – this would help, for case in point, to launch protection leads to get positive buoyancy and rise back to the area.



Just about every of these units would need to have a specific verification (theoretical) and validation (exams) for the distinct atmosphere.
Business off-the-shelf gear can potentially healthy onboard, if a demonstration of physical fitness for objective is manufactured for various scenarios. Nonetheless, most of the exterior components (mainly because of crushing strain) and basic safety devices would warrant custom style and design.
According to experiences, the Titan was using specific “off-the-shelf” products, but it’s challenging to say whether or not this was certified for its intended use at these depths.
Safety units
In the Titan’s case, a tether with the mothership would have ensured fast two-way interaction and a higher facts trade fee. But these cables can get entangled with likely dangers at a shipwreck site.
As this kind of, tethers are mostly used for unmanned cars manned submersibles desire to believe in the pilot. Also, GPS, portable satellite phones and automated identification systems can’t be utilized underwater. These applications use electromagnetic waves that really don’t propagate deep underwater (even though they could be employed on the area).
Some submarines are equipped with a distress beacon, the equal of an crisis position indicating radio beacon (EPIRB). This can be introduced at the captain’s purchase, or through a “dead-man” change if the pilot responds to a exam at common intervals, a unexpected deficiency of response prospects the system to assume the crew is incapacitated.
Ideally, the “banging” appears that have been noted are the Titan’s crew and passengers banging towards the stress hull each 30 minutes. This is a system taught to army submarine crew when grounding on the sea floor.
A substantial-frequency acoustic pinger would be even more effective, as this would present directional precision to property on to a distressed submersible.
There are a range of scenarios that can unfold on the area as well, in the case that the Titan has floated its way up. Even if has (or will do so), the crew and passengers cannot open the vessel’s bolted hatch. They would possible have to go on to contend with the possibly fouled environment within.
Further more complicating issues is the Titan’s white color, which would make it tougher to place in the foaming sea. This is why floating property detected from above are typically in orange or yellow shades allowing for greater visibility.
The upcoming of deep-sea submersibles
Ideally, the crew and travellers of the Titan will be rescued. But if the worst occurs, forensic examination will inevitably glimpse into irrespective of whether the Titan achieved the primary thresholds to demonstrate seaworthiness.
Whilst numerous classification societies suggest a established of guidelines for commercial submarines and submersibles, opting to adhere to these guidelines stays a voluntary process (which the asset’s insurance company normally pushes for).
It is time to accept that likely deep is as complicated, if not additional complex, than heading into area – and that guaranteeing the safety of submersibles should to be more than a make a difference of selection.
This post was at first revealed on The Conversation. Study the first short article.
[ad_2]
Supply link