[ad_1]
A planetary technique is shaped at the boundary of order and chaos. It commences out as a molecular cloud—a massive, cold clump of generally hydrogen fuel that can collapse to make stars. As central stars variety, the remainder of the cloud flattens into a whirling protoplanetary disk that weaves together worlds from turbulent swirls of fuel, ice and dust. From there greater-scale chaos can ensue as bigger planets push smaller types close to. The large planets brawl amongst by themselves, also, competing to rake up excess materials and expand extra giant nevertheless, occasionally ejecting the unfortunate losers from the program in a “last planets standing” melee.
Researchers had extended thought our have photo voltaic system—an “ordered” arrangement of very small orbs closer to the solar and significant ones farther out—was a common final result of this sophisticated process. But NASA’s planet-searching Kepler mission revealed that most units do not resemble our individual at all, instead possessing “similar” configurations of carefully packed worlds all nearly the similar sizing and mass, like peas in a pod.
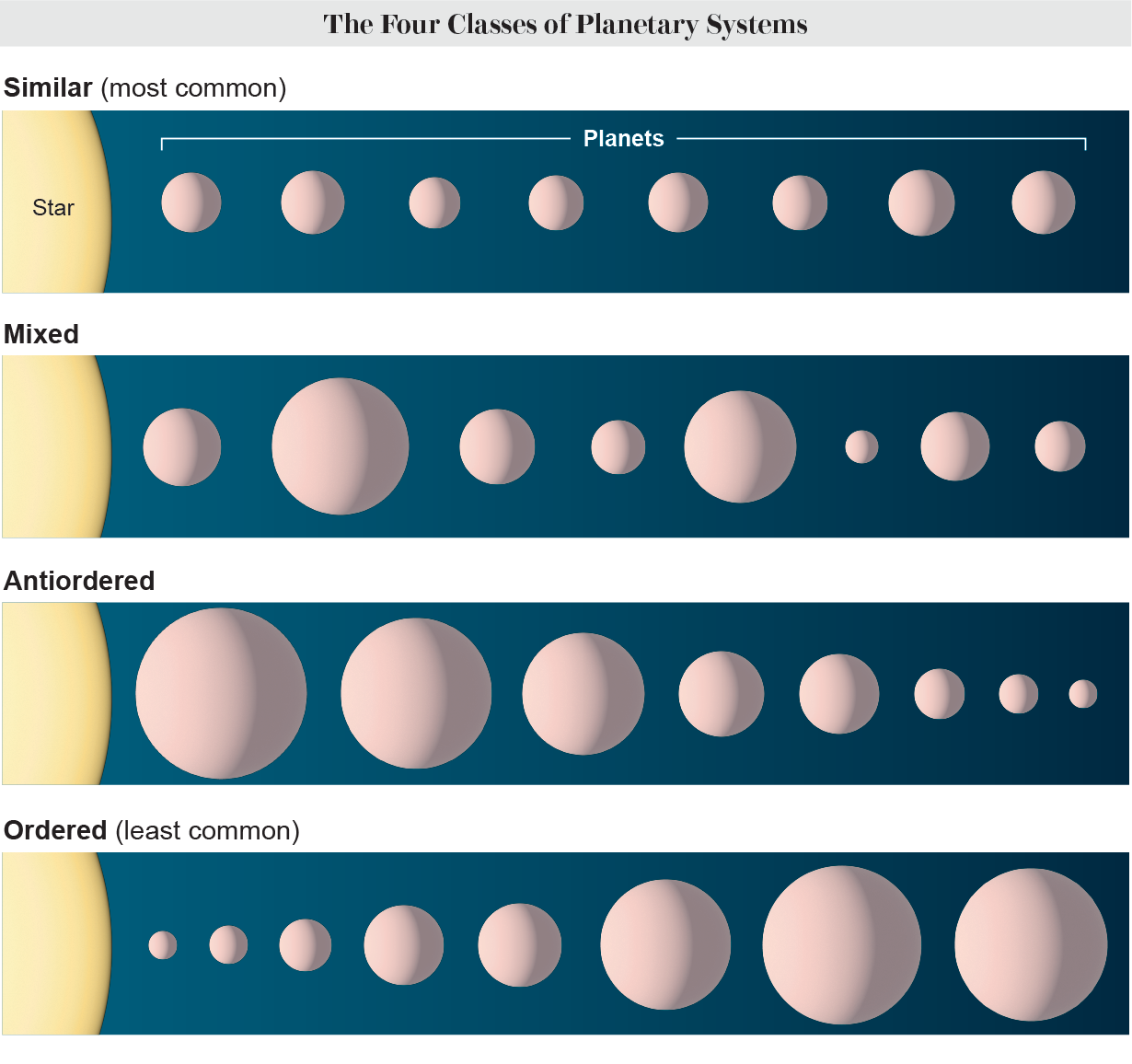


This disparity inspired astrophysicists Lokesh Mishra, now at IBM, Yann Alibert of the College of Bern and their colleagues to investigate what other architectures may exist. This is a formidable undertaking for modern day telescopes but a dilemma that pc designs can quickly take a look at. By their research they famous a 3rd program form in the observational data—a “mixed” distribution of shuffled smaller and substantial planets—and their simulations predicted one far more: an “antiordered” architecture of worlds that get smaller sized and considerably less massive the farther they are from their star. These results, which appear in two research in Astronomy & Astrophysics, fortify the summary that similar architectures are most prevalent and counsel that requested systems like our very own are the rarest. “In a several several years, I think, we’ll have one thing like a ‘standard model’ of planetary formation,” Mishra suggests. “And how various architectures of planetary programs emerge is a concern that any typical model will have to response.”
Crucially, this exploration introduces a new mathematical framework for quantifying similarities among a system’s planets according to any observable characteristic, these as mass or size just one amount reveals the whole range of values for that attribute amid the planets, and the other demonstrates how extensively all those values usually differ from world to earth. This can aid uncover designs that expose broad procedures governing the start and expansion of planetary systems—as properly as wherever those people orderly principles split down. Matching their model’s predictions to observations indicates, for instance, that similar systems’ pea-pod planets arise from sedate, lower-mass protoplanetary disks, with larger-mass disks extra easily producing major planets—like our personal system’s Jupiter—that can chaotically interact to yield the a few other architectures. The strong James Webb Area Telescope and other facilities may possibly soon be equipped to take a look at some of these ideas.
University of Chicago astrophysicist Daniel Fabrycky, who was not included with the new study, says these kinds of approaching observations make these types of scientific studies specifically beneficial. “This is about making some set of principles, around which we anticipate to be equipped to make appealing conclusions in the foreseeable future,” he states. “And which is generally a very good thought because it can be much more scientifically strong to make predictions and then check them, relatively than observing surprising points and portray on a theoretical gloss afterward.”
[ad_2]
Supply website link



