[ad_1]
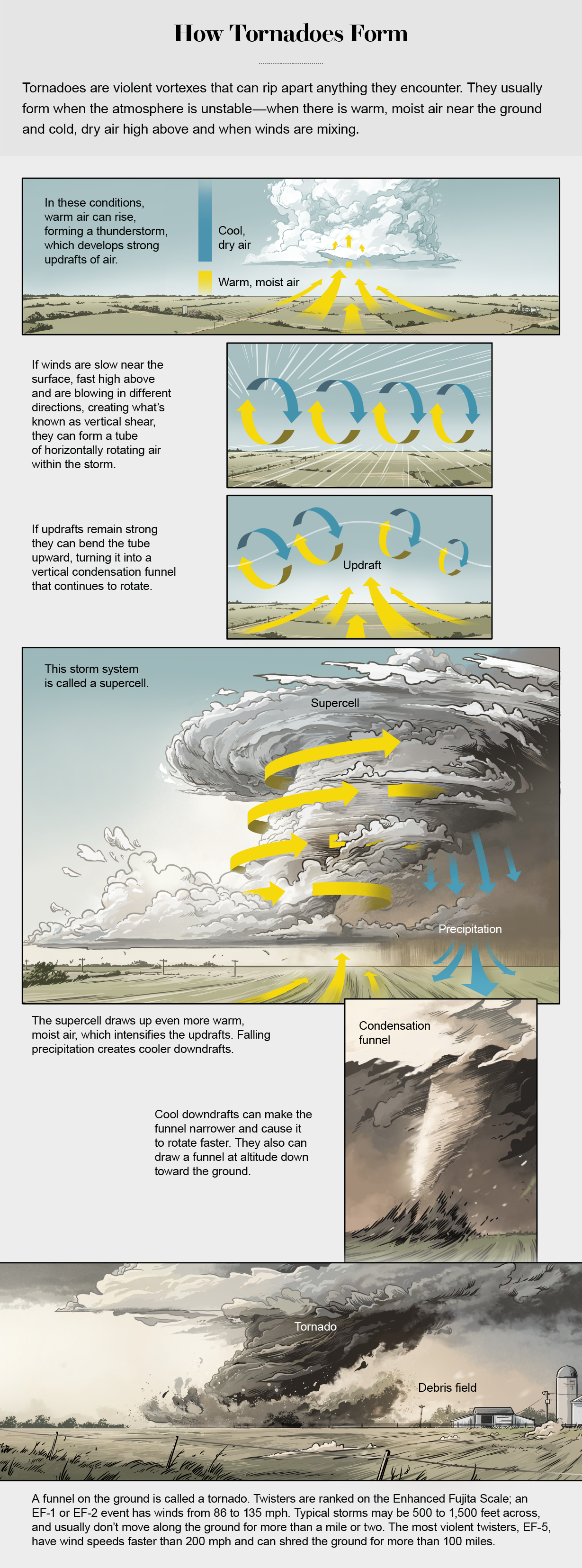
About 1,200 tornadoes strike the U.S. in the course of an typical yr. They are prevalent in the U.S.—far more so than wherever else in the world—because its geography sets up the perfect conditions, specifically in spring and summertime. Westerly winds from the Pacific Ocean drop their humidity when they press up in excess of the Rocky Mountains, getting substantial, dry and awesome as they transfer farther east. Comparable winds may possibly descend from Canada. In the meantime small, heat, humid air streams northward from the Gulf of Mexico. Flat terrain along these paths lets the winds to move comparatively uninterrupted, at contrasting altitudes, until eventually they run into 1 an additional. The angles at which they collide have a tendency to generate unstable air and wind shear, two major factors that favor tornado development. While fairly related air masses do clash in other spots, these kinds of as Uruguay and Bangladesh, the forces are a lot a lot more strong about the U.S. Canada ranks next throughout the world with 100 twisters a yr.


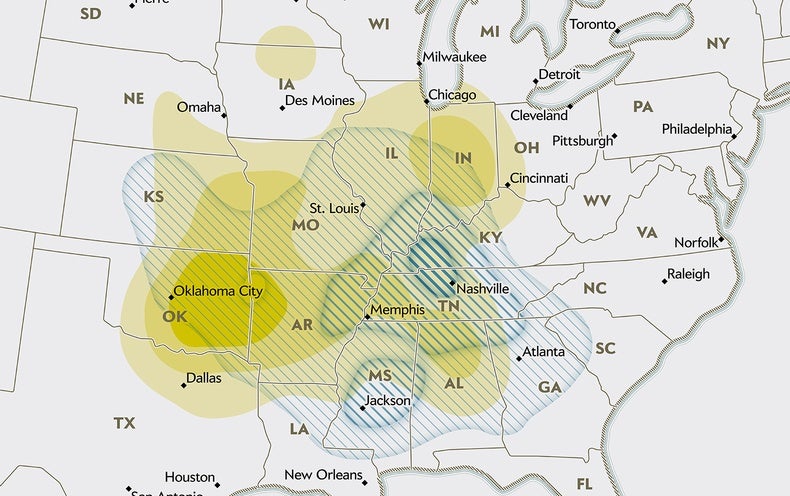
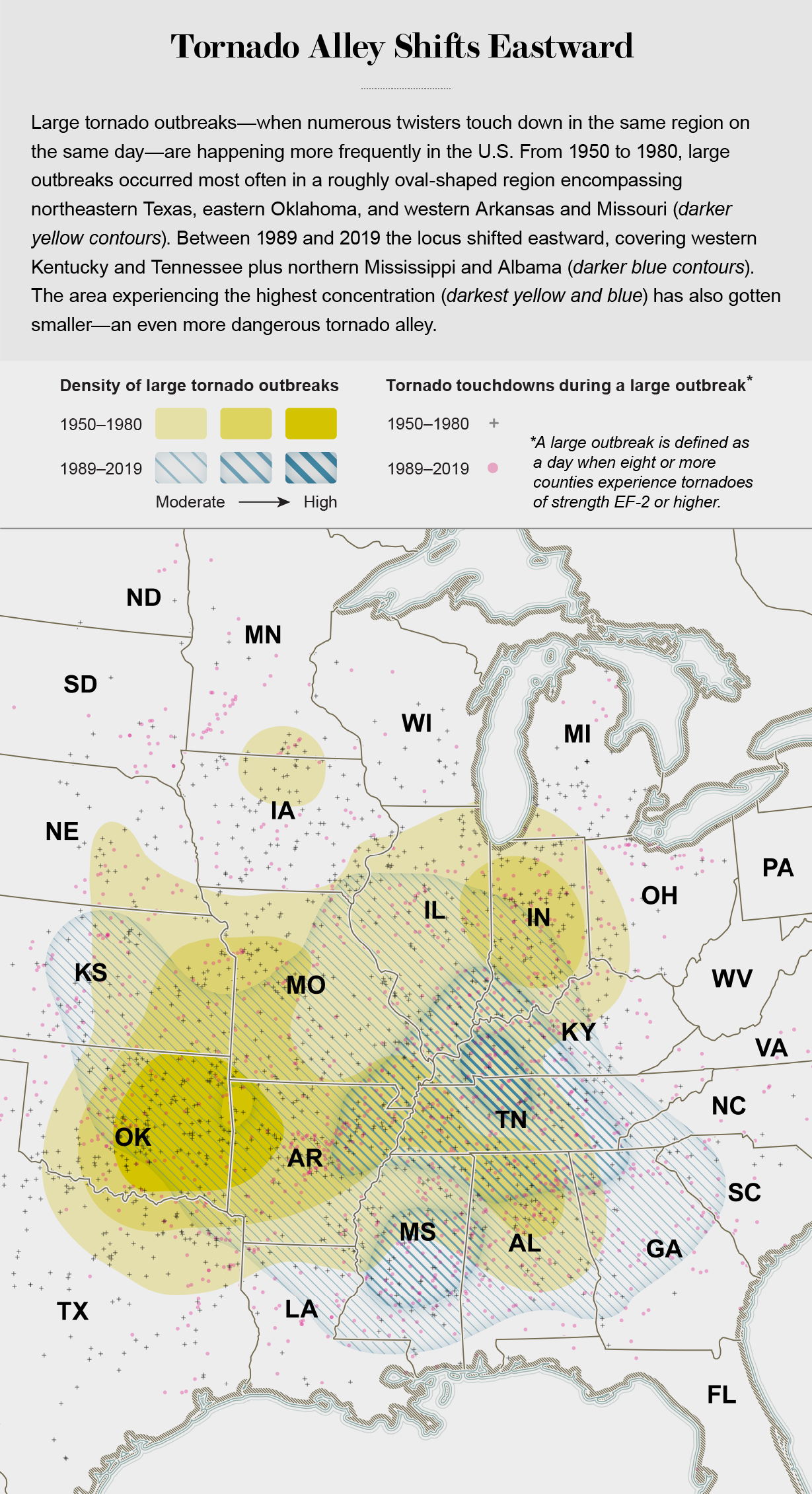
Even though tornadoes touch down in a lot of destinations across the jap 50 % of the place, from the 1950s via the 1990s they struck most normally in Twister Alley, an oval region centered on northeastern Texas and south-central Oklahoma. More just lately, that focus has shifted eastward by 400 to 500 miles. In the previous ten years or so tornadoes have develop into widespread in japanese Missouri and Arkansas, western Tennessee and Kentucky, and northern Mississippi and Alabama—a new area of concentrated storms.


Tornado action in early 2023 epitomized the pattern. A violent twister with wind speeds of 170 miles per hour struck Rolling Fork, Pass up., on March 24, killing at least 26 persons. A week afterwards storms in the new twister alley killed more than 30 people today, and a different team on April 4 broken much more than 80 structures in Bollinger County, Missouri. Those occasions transpired in just the operate-up to peak time in April and Could.
Info collected in the previous two years exhibit that in addition to solo storms, substantial tornado outbreaks—multiple twisters spawned by a solitary weather system—are shifting even extra definitively to the east. The swarms are clustering in a tighter geographical area than in the previous Twister Alley, as well. And outbreaks could be getting fiercer and more regular. “It appears to be like as if we may perhaps be having fewer times in the U.S. with just one tornado and much more days when there are many tornadoes,” suggests Naresh Devineni, an associate professor at City University of New York, who co-led a 2021 geographical assessment of significant twister outbreaks.
Why is this change taking place now? Most frequently tornadoes are made by a supercell—a strong thunderstorm with a rotating updraft of air. Supercells are likely to variety when heat, humid, small-amount air interacts with amazing, dry, higher-amount air, and local weather adjust is building hotter, moister air. Tornadoes also are additional probable to produce when the community environment is unstable, “and warming increases instability,” says Zuohao Cao, a tornado pro at Ecosystem and Weather Alter Canada, who co-led a modern research on storm touchdown spots. Weather adjust is warming the Gulf of Mexico as effectively, which can send out generous quantities of water vapor into the southeastern U.S.
Study suggests that the so-termed dry line is also shifting eastward. The imaginary line operates north from the U.S.-Mexico border up to Canada, dividing the wetter eastern U.S. from the drier western U.S. (To the east, thirsty crops such as corn predominate to the west, drought-tolerant wheat prevails.) The line, which for centuries has fallen approximately together the 100th meridian, has moved east by about 140 miles because the late 1800s. The dry line “can be a boundary for convection—the rising of warm air and sinking of colder air that can gas storms,” wrote Ernest Agee, professor emeritus of atmospheric science at Purdue College, in the Dialogue in 2022.
Climate modify may possibly prolong the usual tornado season as well. Milder winters imply the unstable air masses that can make supercells may possibly become additional likely in March or even earlier in the southeastern U.S.
Twister Alley shifting eastward is far more than a meteorological curiosity. The change is critical: Tornado shelters are common in Texas and Oklahoma but a lot less so elsewhere. The Southeast is far more densely populated, and cell properties, which fare inadequately in windstorms, are much extra popular. Tornadoes in the Southeast also come about at evening much more often than they do farther west, in part since winds can provide sufficient dampness from the Gulf immediately after dim. Scientific tests display that tornadoes that strike at night are 2.5 situations much more likely to bring about fatalities.
Nearby and point out governments in the new bull’s-eye region could possibly want to increase community shelters and warning programs, improve building codes, much better equip unexpected emergency responders, and teach inhabitants about what to do—and not to do—if a tornado is headed their way.
[ad_2]
Supply backlink