[ad_1]
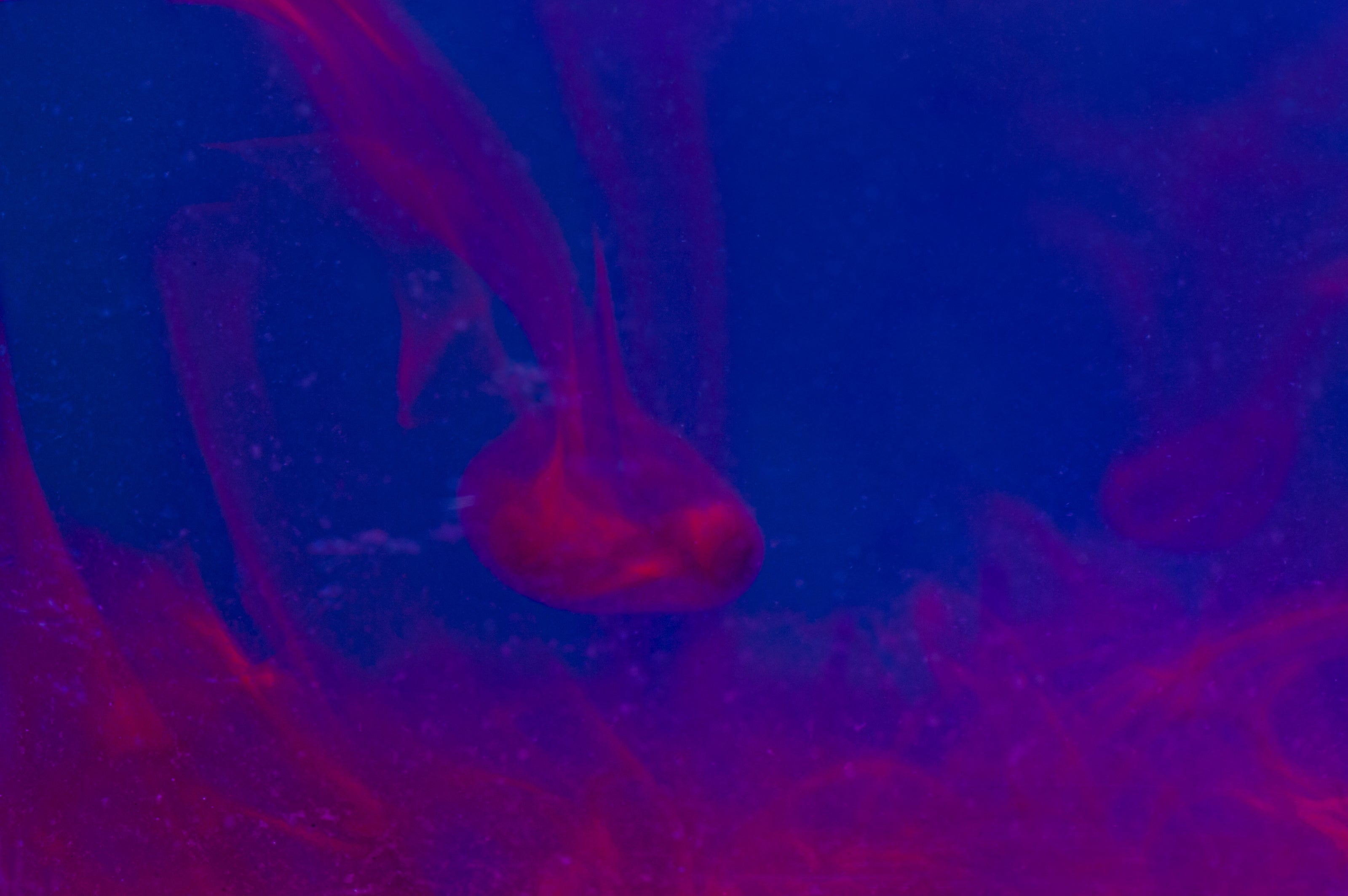

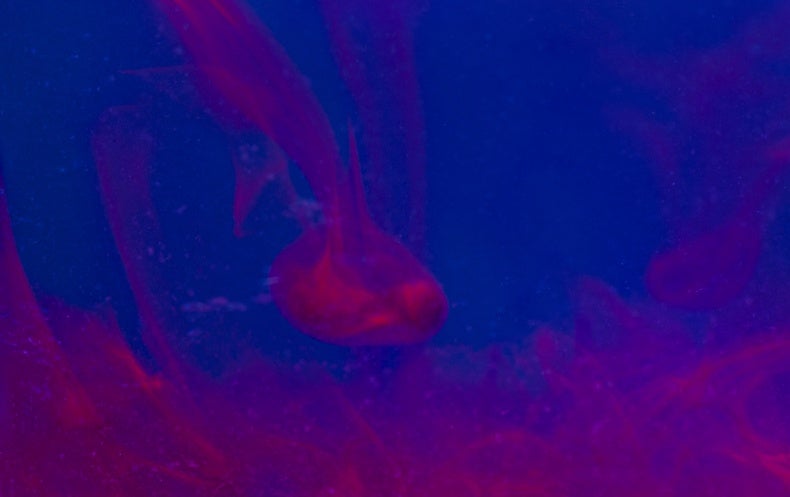
Researchers have developed artificial blobs that resemble a 14-day-outdated human embryo for the to start with time, meaning they can analyze embryo progress past a notably challenging interval of pregnancy.
Traditionally, worldwide procedures reduce exploration on human embryos far more than 14 times soon after fertilization. But the new method utilizes stem cells, which have the prospective to renovate into any other style of cell, this sort of as a coronary heart, skin or even brain mobile, to mimic embryos. And devoid of breaking any guidelines, the final result would make it possible for researchers to superior realize later levels of human progress, in accordance to Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz, a developmental and stem cell biologist at the University of Cambridge and the California Institute of Know-how. She states she’s significantly eager to see these products produced as a result of a section referred to as gastrulation, which occurs about 3 months into human enhancement.
Żernicka-Goetz led the team at the rear of the progress and presented the work on June 14 at the yearly meeting of the Global Society for Stem Cell Study in Boston. Scientific American spoke to Żernicka-Goetz about the research, which she suggests will be released shortly in a scientific journal.
[An edited transcript of the interview follows.]
What precisely did this experiment produce and how?
We merged stem cells to develop embryo versions that establish 3 compartments—to my awareness, for the very 1st time—at postimplantation stages. A single is the embryo. Two are extraembryonic tissues. One is termed trophoblast it’s the tissue that would generally kind placenta. And the 2nd stem cell form forms hypoblastlike tissue, and it’s a tissue that will make a yolk sac.
We not only do not use sperm or egg but also bounce around the initially seven days of growth that take place right before implantation. The structures we assemble appear like embryos that have just implanted. The model is produced until finally the equivalent of day 14 in a human embryo.
With this model, we precisely desired to have an understanding of this peri-implantation stage of progress, when there is cross speak among the three sorts of tissues. What we present with our design for the incredibly to start with time is: we can actually glimpse at this crosstalk and interactions among the tissues. So that’s extremely intriguing.
We do not provide any additional elements to the lifestyle media that we use, which we proven 10 several years back. And in this media, the a few styles of stem cells self-structured to type this embryolike construction.
It’s not an embryo—it’s an embryolike structure. Or in other text, we can contact it a model of a human embryo. It is three-dimensional, its architecture is gorgeous, and it’s incredibly potent in comprehending the results in for pregnancy loss at the time of implantation. But it’s not a genuine embryo.
What type of moral approval method did you go by for this examine?
All scientific studies on human embryos have to be authorised, and our lab has this acceptance to analyze human embryos right up until day 14. But for human embryo stem mobile designs, such as the a single which we designed, investigation on this is authorized since they are not actual human embryos they are human embryo styles.
Is this the to start with time that artificial human embryo types have been developed from stem cells?
It’s not the first time. A couple of decades in the past individuals designed embryo models from stem cells at earlier stages of advancement, preimplantation stage. Our model is distinctive for the reason that it covers later on phases of human embryo advancement, and it is made up of the three lineages, the a few tissues that are incredibly critical at this time.
What do you hope to discover from these versions?
Our enthusiasm for generating these versions is to really fully grasp this developmental black box. This is the time when the embryo implants, and we can’t see it, and it is quite difficult to recognize how tissue interacts.
Seven decades back we printed the first study of human embryo growth [outside of the uterus past] the implantation stage, so for the initial time, we were able to see a actual human embryo establishing as a result of implantation and how various tissues in that embryo produced. This gave us the thought that we may possibly be able, in its place of making use of human embryos, to mimic this cell-cell interaction with stem cells and research human embryo improvement in a design somewhat than in a serious embryo.
Why do I do it? I am fascinated by this stage of progress that’s very difficult to recognize. It is predicted that 30 % of pregnancies fall short quickly soon after implantation. So this design will make it possible for us to have an understanding of the good reasons guiding that failure. Ideally, with time, we will be equipped to conserve the life of those embryos.
[ad_2]
Supply url