[ad_1]
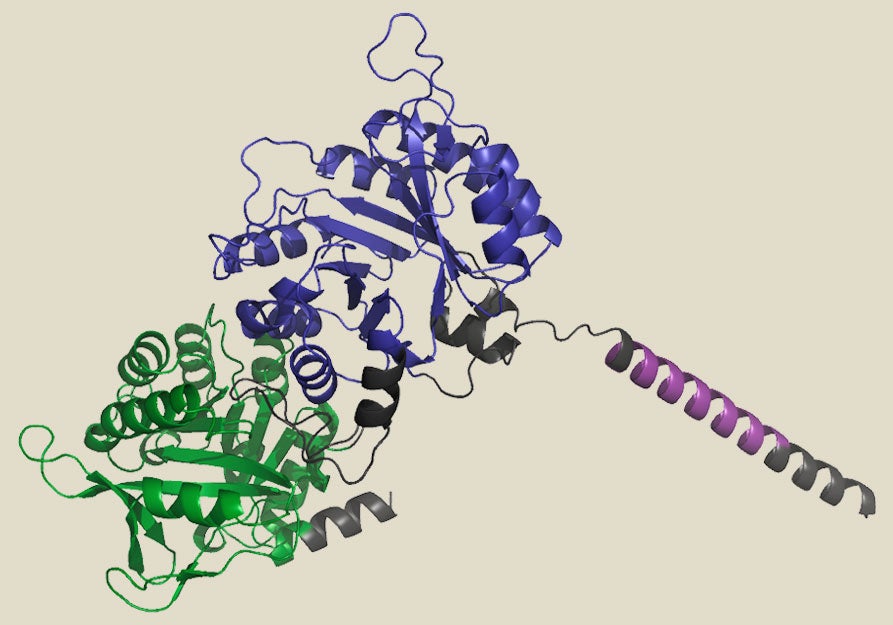
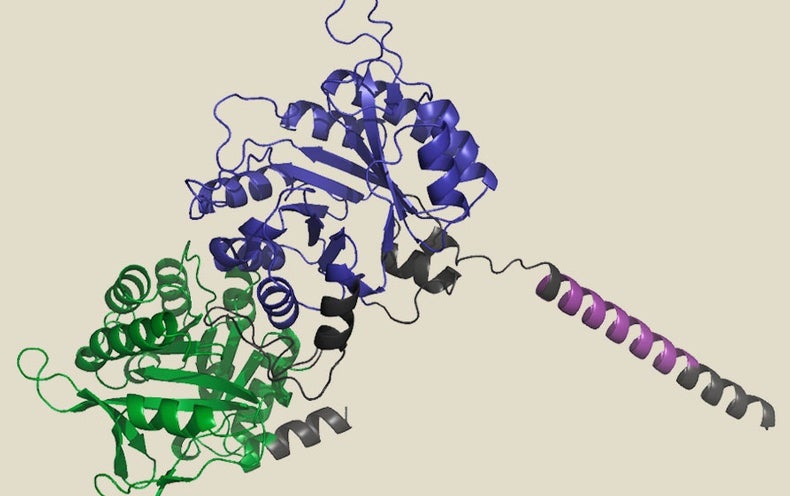
Machine learning (ML) and other AI- dependent computational applications have proven their prowess at predicting true-environment protein structures. AlphaFold 2, an algorithm developed by experts at DeepMind that can confidently predict protein structure purely on the basis of an amino acid sequence, has develop into pretty much a household name considering that its start in July 2021. Nowadays, AlphaFold 2 is applied routinely by many structural biologists, with above 200 million buildings predicted.
This ML toolbox appears capable of producing built-to-buy proteins too, together with all those with capabilities not present in character. This is an captivating prospect mainly because, regardless of organic proteins’ extensive molecular diversity, there are lots of biomedical and industrial troubles that evolution has under no circumstances been compelled to solve.
Experts are now promptly relocating toward a potential in which they can use very careful computational analysis to infer the underlying principles governing the framework and function of genuine-world proteins and utilize them to construct bespoke proteins with features devised by the person. Lucas Nivon, CEO and cofounder of Cyrus Biotechnology, thinks the ultimate affect of this kind of in silico-developed proteins will be huge and compares the area to the fledgling biotech field of the 1980s. “I believe in 30 many years 30, 40 or 50 per cent of medicines will be computationally designed proteins,” he claims.
To date, corporations working in the protein style and design place have largely focused on retooling current proteins to carry out new tasks or boost certain properties, relatively than genuine design and style from scratch. For illustration, researchers at Produce Biomedicines have drawn on present awareness about the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and its interactions with the receptor protein ACE2 to style and design a synthetic protein that can continually block viral entry throughout numerous variants. “In our inner tests, this molecule is rather resistant to all of the variants that we’ve noticed so far,” says cofounder and main technologies officer Gevorg Grigoryan, adding that Deliver aims to use to the Fda to distinct the way for clinical tests in the second quarter of this calendar year. Far more formidable applications are on the horizon, while it stays to be noticed how shortly the leap to de novo design—in which new proteins are built fully from scratch—will occur.
The discipline of AI-assisted protein layout is blossoming, but the roots of the industry stretch again a lot more than two decades, with operate by tutorial researchers like David Baker and colleagues at what is now the Institute for Protein Style at the University of Washington. Setting up in the late 1990s, Baker—who has co-launched businesses in this house such as Cyrus, Monod and Arzeda —oversaw the growth of Rosetta, a foundational software suite for predicting and manipulating protein structures.
Due to the fact then, Baker and other scientists have formulated quite a few other impressive equipment for protein layout, driven by fast progress in ML algorithms—and notably, by improvements in a subset of ML approaches recognised as deep discovering. This previous September, for illustration, Baker’s staff posted their deep studying ProteinMPNN platform, which enables them to enter the composition they want and have the algorithm spit out an amino acid sequence possible to create that de novo framework, accomplishing a increased than 50 per cent achievement charge.
Some of the greatest pleasure in the deep discovering earth relates to generative styles that can develop fully new proteins, in no way viewed before in mother nature. These modeling applications belong to the identical group of algorithms utilized to make eerie and persuasive AI-created artwork in courses like Secure Diffusion or DALL-E 2 and text in programs like chatGPT. In all those circumstances, the software package is qualified on extensive amounts of annotated impression information and then uses all those insights to generate new images in response to user queries. The exact same feat can be achieved with protein sequences and structures, exactly where the algorithm attracts on a wealthy repository of serious-world organic info to desire up new proteins dependent on the patterns and ideas noticed in character. To do this, on the other hand, researchers also have to have to give the computer steerage on the biochemical and bodily constraints that advise protein layout, or else the ensuing output will offer you little a lot more than creative value.
1 efficient tactic to fully grasp protein sequence and framework is to method them as ‘text’, employing language modeling algorithms that stick to principles of organic ‘grammar’ and ‘syntax’. “To create a fluent sentence or a doc, the algorithm requires to study about relationships involving distinct types of phrases, but it desires to also understand points about the earth to make a doc that is cohesive and would make sense,” says Ali Madani, a computer scientist previously at Salesforce Exploration who not too long ago started Profluent.
In a the latest publication, Madani and colleagues describe a language modeling algorithm that can produce novel laptop-developed proteins that can be successfully generated in the lab with catalytic things to do similar to people of organic enzymes. Language modeling is also a crucial section of Arzeda’s toolbox, according to co-founder and CEO Alexandre Zanghellini. For just one undertaking, the organization employed many rounds of algorithmic style and optimization to engineer an enzyme with improved stability from degradation. “In a few rounds of iteration, we ended up ready to go from comprehensive disappearance of the protein following 4 weeks to retention of successfully 95 per cent activity,” he claims.
A latest preprint from researchers at Crank out describes a new generative modeling-primarily based style algorithm known as Chroma, which involves numerous functions that enhance its functionality and achievements price. These include diffusion styles, an solution utilised in quite a few image-technology AI tools that can make it less complicated to manipulate advanced, multidimensional facts. Chroma also employs algorithmic techniques to assess extended-range interactions involving residues that are significantly apart on the protein’s chain of amino acids, referred to as a spine, but that may perhaps be critical for appropriate folding and operate. In a series of first demonstrations, the Generate staff confirmed that they could attain sequences that ended up predicted to fold into a broad array of naturally occurring and arbitrarily preferred structures and subdomains—including the designs of the letters of the alphabet—although it remains to be found how many will type these folds in the lab.
In addition to the new algorithms’ energy, the huge sum of structural info captured by biologists has also authorized the protein layout discipline to acquire off. The Protein Details Bank, a important resource for protein designers, now incorporates more than 200,000 experimentally solved constructions. The Alpha-Fold 2 algorithm is also proving to be a sport changer listed here in phrases of giving schooling product and steering for design algorithms. “They are designs, so you have to just take them with a grain of salt, but now you have this terribly massive sum of predicted structures that you can make upon,” suggests Zanghellini, who states this device is a core element of Arzeda’s computational structure workflow.
For AI-guided style, a lot more education info are usually much better. But existing gene and protein databases are constrained by a confined variety of species and a hefty bias in the direction of individuals and usually utilized design organisms. Basecamp Research is developing an extremely-diverse repository of biological facts received from samples gathered in biomes in 17 nations around the world, ranging from the Antarctic to the rainforest to hydrothermal vents on the ocean flooring. Main technological know-how officer Philipp Lorenz suggests that after the genomic facts from these specimens are analyzed and annotated, they can assemble a information-graph that can expose useful relationships concerning various proteins and pathways that would not be clear purely on the foundation of sequence-based mostly analysis. “It’s not just creating a new protein,” states Lorenz. “We are discovering protein people in prokaryotes that have been considered to exist only in eukaryotes.” [Prokaryotes, single-celled organisms such as bacteria, lack the more sophisticated internal cellular structures found in eukaryotes, which are capable of becoming multicellular organisms.]
This signifies many additional beginning details for AI-guided protein style and design initiatives, and Lorenz states that his team’s very own layout experiments have accomplished an 80 % accomplishment level at creating purposeful proteins.
But proteins do not purpose in a vacuum. Tess van Stekelenburg, an trader at Hummingbird Ventures, notes that Basecamp, one particular of the organizations funded by the business, captures all way of environmental and biochemical context for the proteins it identifies. The ensuing ‘metadata’ accompanying each protein sequence can assistance guideline the engineering of proteins that express and perform optimally in unique ailments. “It presents you a large amount a lot more means to constrain for points like pH, temperature or strain, if that’s what you are planning to search at,” she claims.
Some businesses are also seeking to increase community structural biology assets with details of their own. Generate is in the method of setting up a multi-instrument cryo-electron microscopy facility, which will allow for them to crank out around-atomic-resolution buildings at somewhat substantial throughput. These internally created structural details are additional probable to include things like relevant metadata about individual proteins than knowledge from publicly obtainable resources.
In-house soaked lab amenities are yet another vital component of the layout course of action mainly because experimental outcomes are, in switch, made use of to train the algorithm to attain even better outcomes in upcoming rounds. Grigoryan notes that, though Create likes to highlight its algorithmic resource- box, the greater part of its workforce includes experimentalists.
And Bruno Correia, a computational biologist at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, says that the achievements of a protein structure effort and hard work relies upon on close session concerning algorithm experts and skilled soaked-lab practitioners. “This notion of how protein molecules are and how they behave experimentally builds in a good deal of constraints,” says Correia. “I imagine it is a blunder to take care of biological entities just as a piece of facts.”
Organic validation is an particularly essential thought for buyers in this sector, claims van Stekelenburg. “If you are carrying out de novo, the genuine gold typical is not which architecture are you using—it’s what percentage of your created proteins experienced the close wished-for assets,” she says. “If you simply cannot display that, then it doesn’t make perception.” Accordingly, most organizations pursuing computational design and style are continue to concentrated on tuning protein function instead than overhauling it, shortening the leap between prediction and overall performance.
Nivon says that Cyrus ordinarily functions with current medications and proteins that slide limited in a unique parameter. “This could be a drug that wants improved efficacy, decrease immunogenicity or a greater toxicity profile,” he states. For Cradle, the most important target is to make improvements to protein therapeutics by optimizing qualities like security. “We’ve benchmarked our product towards empirical experiments so that men and women can get a sense of how effectively this could work in an experimental location,” states founder and CEO Stef van Grieken.
Arzeda’s target is on enzyme engineering for industrial purposes. They have by now succeeded in creating proteins with novel catalytic features for use in agriculture, products and meals science. These initiatives normally start off with a somewhat well-set up main reaction that is catalyzed in nature. But to adapt these reactions to function with a different subtrate, “you will need to remodel the energetic site significantly,” claims Zanghellini. Some of the company’s initiatives include a plant enzyme that can split down a broadly used herbicide, as perfectly as enzymes that can transform comparatively reduced-value plant byproducts into useful natural sweeteners.
Generate’s to start with-generation engineering jobs have focused on optimization. In one particular posted review, business researchers showed that they could “resurface” the amino acid-metabolizing enzyme l-asparaginase from Escherichia coli microorganisms, altering the amino acid composition of its exterior to considerably minimize its immunogenicity. But with the new Chroma algorithm, Grigoryan suggests that Crank out is all set to embark on more bold initiatives, in which the algorithm can start off creating correct de novo designs with consumer-specified structural and practical options. Of training course, Chroma’s layout proposals need to then be validated by experimental tests, though Grigoryan says “we’re very encouraged by what we have seen.”
Zanghellini believes the industry is around an inflection issue. “We’re beginning to see the chance of actually truly producing a elaborate lively web site and then creating the protein about it,” he states. But he adds that many far more troubles await. For case in point, a protein with outstanding catalytic qualities may well be exceedingly complicated to manufacture at scale or exhibit bad properties as a drug. In the long term, on the other hand, upcoming-technology algorithms need to make it feasible to crank out de novo proteins optimized to tick off a lot of containers on a scientist’s desire listing relatively than just a person.
This short article is reproduced with permission and was first printed on February 23, 2023.
[ad_2]
Resource connection