[ad_1]
Is the sunlight an only little one? Or was it born into a (pretty, very) large relatives?
The answer tells us a lot more than just how uncomfortable getaway family reunions can be (if you assume yours are undesirable, picture how a great deal even worse it would be with a several thousand sibling rivals). Just after all, the sun’s origin tale is, in the long run, our own. We have witnessed substantial leaps in our understanding of how stars variety, but, ironically, we nevertheless have some quite basic concerns left about our nearest, dearest one. This sort of as, irrespective of whether the sunlight was born solo or along with a enormous passel of other stars.
Irrespective of the sunlight staying shut enough that we can nearly contact it, the most significant problem with getting its origin tale is that it is old. Born 4.6 billion yrs in the past, our star is effectively into middle age and has wandered much from its ancestral home—some anonymous, now-vanished “stellar nursery” of gas that long back dispersed or consolidated into stars.
We just cannot come across that nursery, but we can even now learn about it. We have some evidence of it, maybe remarkably, in the kind of meteorites, some of which continue to have clues about the gestational setting close to them through the beginning of the photo voltaic system. For case in point, isotopes of aspects like potassium inside of meteorites have informed us in which in the presolar nebula they shaped, and variations between meteorites can be employed to help establish the nebula’s problems properly prior to the emergence of any planets.
With details from meteorites in hand and aided by point out-of-the-art computer system simulations, an global crew of astronomers investigated the probably natal atmosphere of the sunlight and not long ago released its final results in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Modern society. Making use of a clever line of reasoning, their investigation implies the sunlight not only had several siblings but spawned in rather a metropolitan neighborhood.
Stars are born in cosmic clouds referred to as nebulae, forming when their interiors collapse on to a central pilelike issue that gets to be the nascent star. Nebulae come in quite a few styles and sizes, from compact darkish globules to enormous large molecular clouds. How a star forms in any given nebula is significantly far more a tale of character than of nurture.

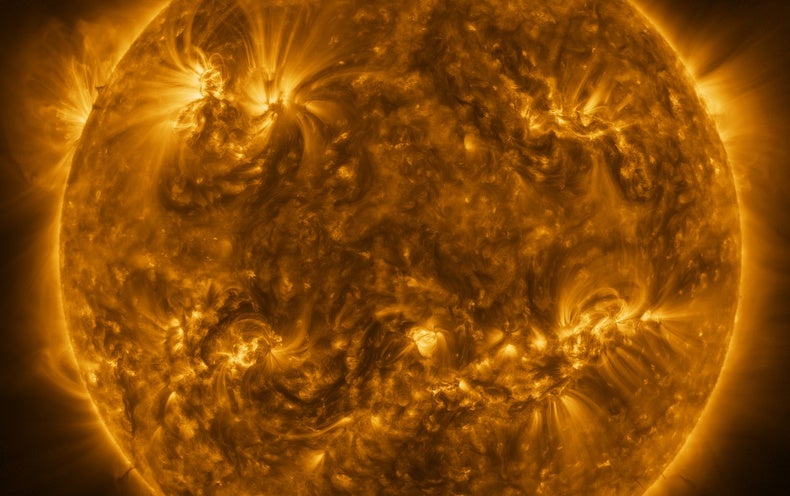
For illustration, the close by nebula Barnard 68 is a darkish clot of chilly gasoline and dust—tiny grains of silicates (rocky material) and intricate carbon molecules related to soot—relatively close to us in space, only a several hundred light-weight-a long time away. It is a person of my preferred objects an eerie, pitch-black ghostly mass that completely blocks all light from stars at the rear of it, like an opaque hole in the sky.
It is only 50 percent a light-yr throughout (just about three trillion miles), with scarcely sufficient substance in it to make a single star marginally heftier than the sunlight. It is probably in the middle of that process now, and could transmogrify by itself into a star in as little as 200,000 many years.
On the other end of the scale, we have the Orion B molecular cloud elaborate, a definitely massive website of energetic star development that’s around a thousand gentle-yrs absent and numerous hundreds of gentle-many years across. It is beefy ample to make a staggering selection of stars—at least 100,000 like the sunshine. The iconic Orion nebula, obvious to the naked eye and the birthplace of hundreds of stars, is only just one smaller section of this enormous stellar manufacturing facility.
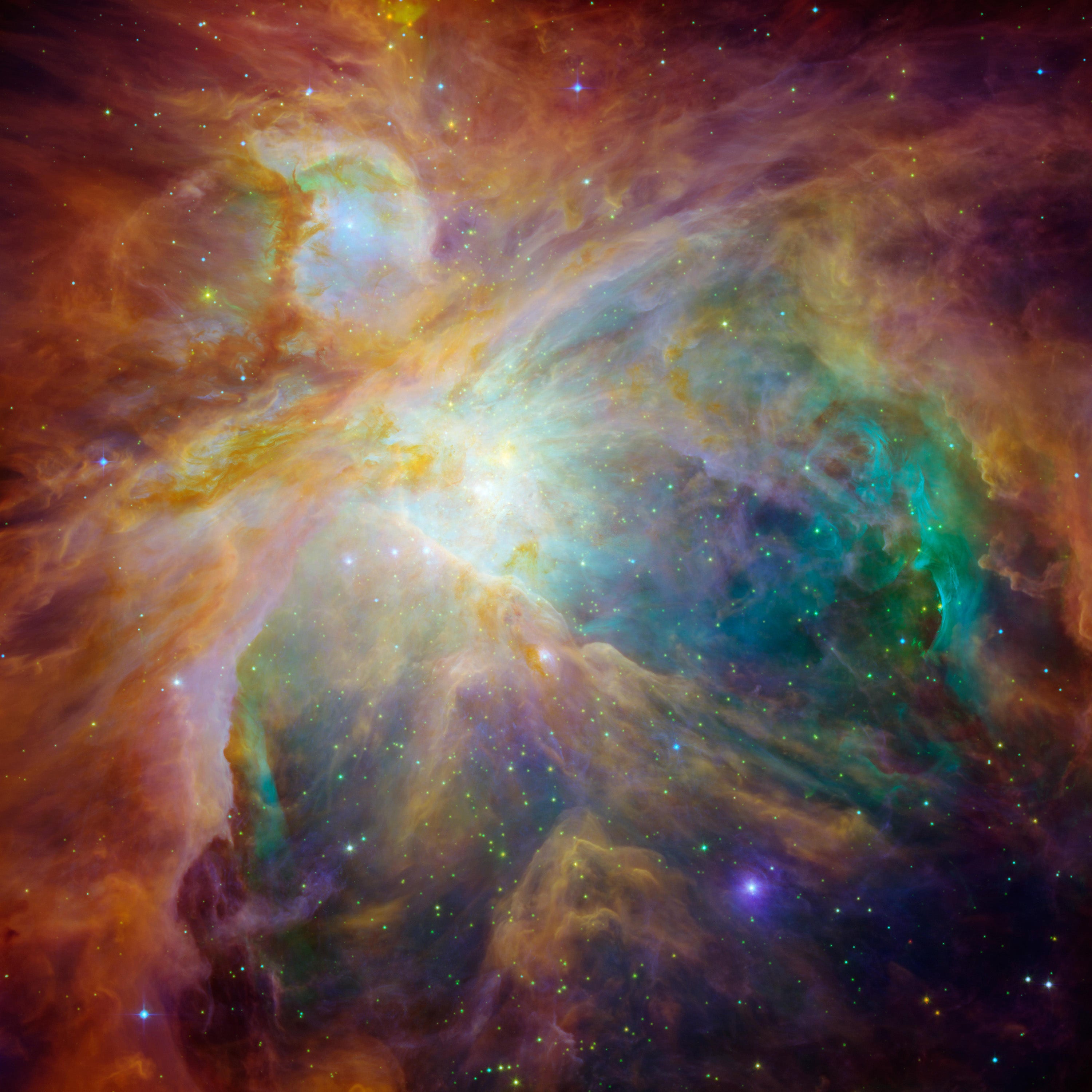
 

Giant clouds like this are rather scarce but crank out stars on an industrial scale, whilst the lesser clouds are a lot less fecund but litter the galaxy. Just searching at individuals quantities statistically it is not feasible to discern the origin of the solar: it could have arrive from either variety of stellar nursery.
On the other hand, these nebular environments are vastly different, which influences the stars they create. Enormous stars found in a nebula have a massive influence on their gestating siblings. They can blast out fierce winds of subatomic particles—like the photo voltaic wind but ramped up way earlier 11. These winds can seed forming stars with major elements like aluminum and magnesium. And later on, when they explode as supernovae, they fling a distinctive combine of these aspects, such as iron and cobalt, a pretty prolonged way.
Enormous stars, however, are exceptional. Perhaps just one out of a hundred stars is huge ample to hold this form of sway, and small nebulae simply really don’t make them. That implies, in basic principle, searching at the chemical composition of the early solar system could notify us in what kind of nursery the sun was born.
This was the aim of the freshly revealed analysis. The astronomers appeared at two features in specific: aluminum-26 and iron-60. Aluminum-26 is developed inside large stars and blown out in their winds, while iron-60 is solid in the thermonuclear hell of an exploding star. The two aspects are radioactive, decaying into magnesium and cobalt, so very carefully measuring the quantities of these daughter factors in pristine samples from the earliest days of the solar system—from meteorites, that is—can tell us about the ecosystem in which the sun formed.
For their new evaluation, the global group of scientists employed the physics of nebulae and star development to simulate a sunlike star’s beginning in a assortment of environments, from nebulae that contains very couple of stars (a proxy for smaller sized clouds) up to massive kinds with lots of thousands. Future, they calculated the elemental composition of the proto-proxy-presolar disk that emerged in just about every one particular, then when compared these digital yields in opposition to what’s in fact measured in meteorites.
Their outcomes point out that as it shaped in its natal disk, the early solar was possible pummeled by impressive winds and supernovae explosions—both sourced from significant stars. That implies the solar nursery was much more like the Orion complex than Barnard 68.
In other words and phrases, the sunlight was likely much more of a downtown city kid than a rural compact-town star. Of study course, with its nebular nursery gone, we can’t ensure this quickly. Soon after all, you just cannot go property once again.
And what of the sun’s siblings, the thousands of other stars in its prolonged loved ones? Like the sun, they once nestled together like a litter of puppies, but very likely wandered out on their individual eons back, and are now orphaned, scattered across the galaxy. Continue to, astronomers do glimpse for them—ones with the exact same age and composition as the sun—so that we can discover more about our mum or dad star.
A reunion is very unlikely. If we want to see a family members album, we’ll just have to set it alongside one another ourselves.
This is an belief and assessment write-up, and the sights expressed by the author or authors are not automatically all those of Scientific American.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink


