[ad_1]

The first asteroid belt at any time uncovered outside the house the photo voltaic method is additional advanced than predicted, new observations by the James Webb Room Telescope (JWST) expose.
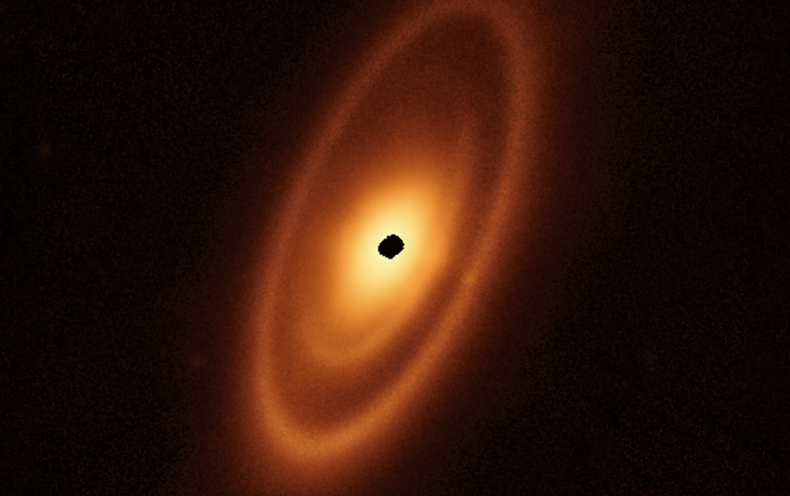
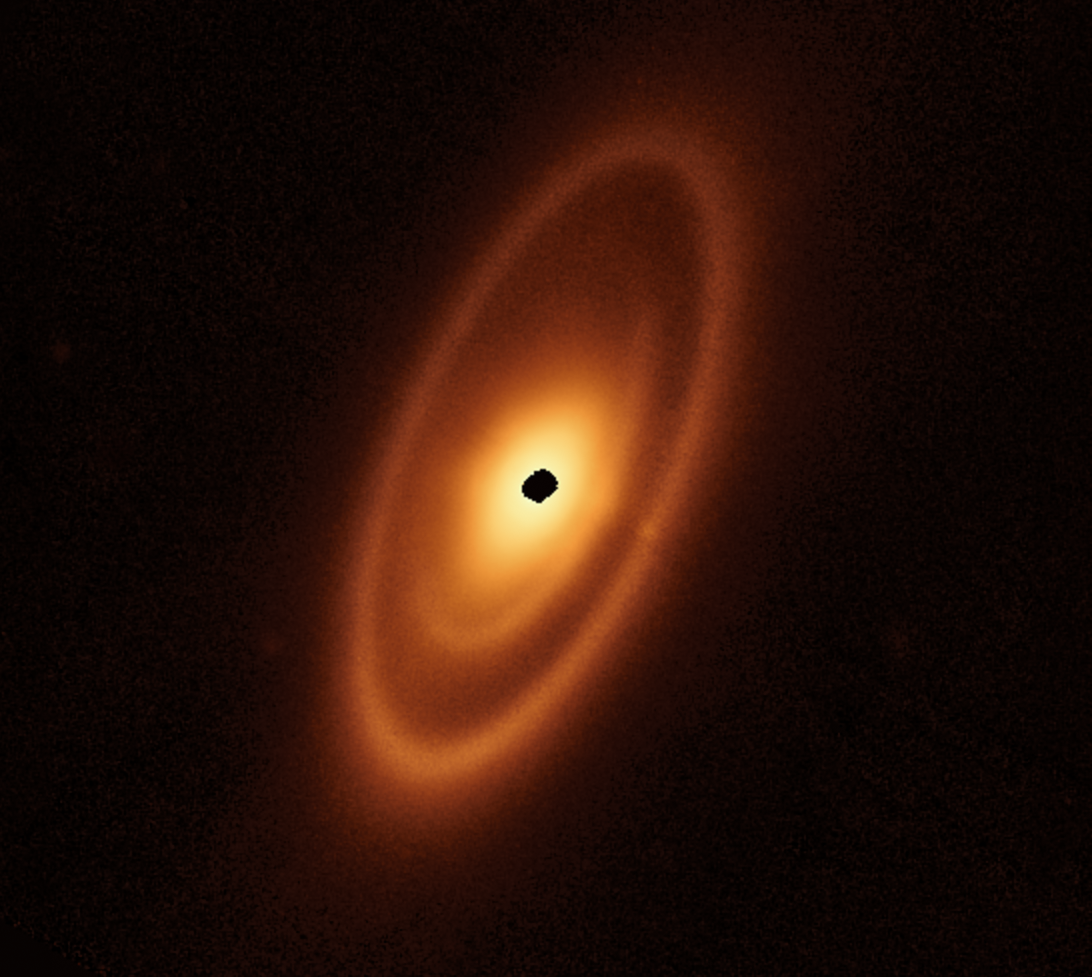
Astronomers used JWST to examine the dusty ring technique around Fomalhaut, a younger, hot star that lies about 25 gentle-many years from Earth and is seen with the bare eye in the constellation Piscis Austrinu, the Southern Fish.
Fomalhaut’s ring process is made up of 3 nested belts that increase out for all over 14.3 billion miles (23 million kilometers) — about 150 times the length involving Earth and the sunlight. The rings are additional complicated than possibly the Kuiper Belt, a ring of frigid bodies beyond Neptune, or the main asteroid belt, which sits concerning Jupiter and Mars, the new JWST observations clearly show.
Astronomers learned a dusty structure encompassing Fomalhaut in 1983 working with NASA’s Infrared Astronomical Satellite. Yet the two internal belts of this procedure experienced hardly ever been sighted in advance of this observation with the JWST.
The dust belts around the young star are considered to be particles from collisions among larger bodies like asteroids and comets, and are for that reason referred to as “particles disks.” These disks are various than protoplanetary disks, which keep material that later gloms jointly to kind planets. Debris disks variety later, following planets are in area.
“I would explain Fomalhaut as the archetype of particles disks discovered somewhere else in our galaxy, mainly because it has parts comparable to these we have in our very own planetary technique,” András Gáspár of the University of Arizona, the guide author of a study saying the new benefits, reported in a assertion.
“By hunting at the designs in these rings, we can truly get started to make a tiny sketch of what a planetary program should to glimpse like — if we could essentially get a deep sufficient image to see the suspected planets,” Gáspár additional.
Fomalhaut’s outermost belt, which is two times as substantial as the Kuiper Belt, has been imaged previously by the Hubble Space Telescope, the Herschel House Observatory and the ground-dependent Atacama Big Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). None of all those devices were being ready to see the interior framework in just the outer belt, however.
“In which the JWST actually excels is that we’re capable to bodily solve the thermal glow from dust in these inner regions. So you can see interior belts that we could by no means see before,” research crew member Schuyler Wolff, also of the College of Arizona, claimed in the very same assertion.
Likely forward, astronomers hope to graphic particles disks like Fomalhaut’s around other stars making use of JWST.
“With Hubble and ALMA, we were being equipped to graphic a bunch of Kuiper Belt analogs, and we’ve realized masses about how outer disks kind and evolve,” Wolff ongoing. “But we need to have the JWST to permit us to graphic a dozen or so asteroid belts in other places. We can study just as considerably about the internal heat areas of these discs as Hubble and ALMA taught us about the colder outer regions.”
Just like Jupiter dominates the main asteroid belt and Neptune sculpts the Kuiper Belt, astronomers consider that particles disks exterior the solar procedure may possibly be shaped by unseen planets. That implies there may well perfectly be a planet or two lurking in the rings around Fomalhaut.
“We absolutely failed to be expecting the more elaborate framework with the next intermediate belt and then the broader asteroid belt,” Wolff said. “That structure is quite fascinating, simply because any time an astronomer sees a gap and rings in a disk, they say, ‘There could be an embedded planet shaping the rings!'”
One element currently noticed by JWST in the rings may perhaps point out the existence of forming protoplanets. The team noticed what Gáspár labeled “the good dust cloud,” which may possibly stage to a collision in the outer ring of Fomalhaut between two “beneath building” infant planets. This aspect could hence be an increasing cloud of pretty fine dust particles from two icy bodies that smashed into just about every other.
A comparable aspect was spotted in the similar ring by Hubble again in 2008. It had dissipated by the time the area telescope reexamined the ring procedure in 2014, scientists reported.
Further investigations of more devices like Fomalhaut with JWST could reveal how planets transfer by means of these pancake-flat disks. Observing the dust cloud by itself, meanwhile, could expose aspects about the construction of planetary units other than our very own. This contains getting what their asteroids — which are substantially as well smaller to see even with potent instruments like JWST or Hubble — are like, and if they are related to the room rocks that swirl close to our star and its planets.
The team’s research was released on-line Monday (May well 8) in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Copyright 2023 Area.com, a Long term enterprise. All legal rights reserved. This content may possibly not be released, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
[ad_2]
Source connection