[ad_1]
The initial methods to address the millennia-previous thriller of our real location in the universe happened, of all spots, on a brisk and early Tuesday morning in the unremarkable meeting area of a hotel in Washington, D.C. Right here a group of legendary heroes assembled on Halloween—Gandalf and a Star Trek captain among them. Nevertheless these ended up not just costumes donned by trick-or-dealing with experts. They had been a fitting metaphor for the 60 astronomers chosen to get started a single of the grandest duties conceivable, not just in space science but across the spectrum of human historical past: to structure a telescope that can find, or refute, signs of life on planets orbiting other stars. This sort of a purpose appears almost fanciful. Can we in fact develop a multibillion-greenback observatory with a fantastic chance of identifying aliens on worlds beyond the solar process? The answer appears to be that we can, and if a developing checklist of pivotal conclusions can be surmounted, we will. Everyday living may be abundant in the universe or it may possibly be extremely rare—learning which is nearer to the truth would be epochal. By this NASA-led project’s stop, the purpose is to “have plenty of observations to know both way,” says Courtney Dressing of the University of California, Berkeley.
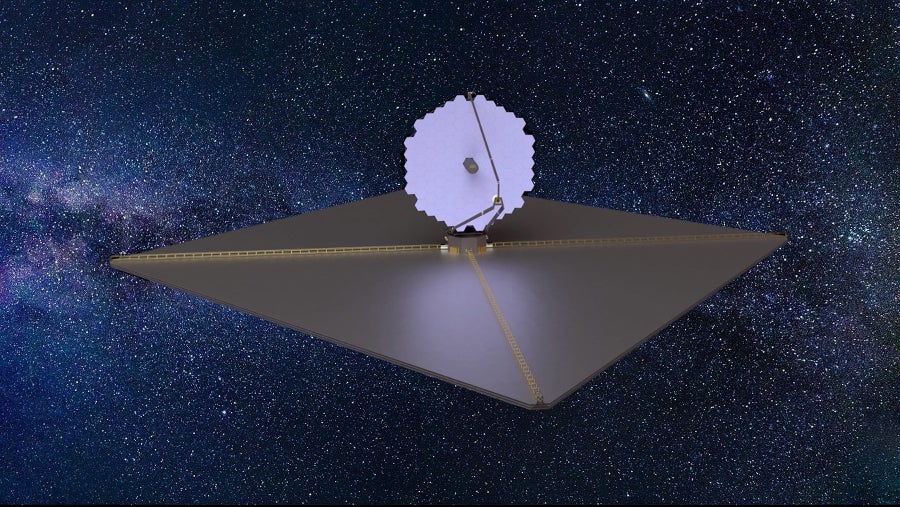
Named the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO) and focused for start all over 2040, this would be by far the most bold and sophisticated telescope nonetheless created. But its major purpose is pretty much childishly simple—to hunt for daily life on 25 Earth-like worlds. “This is the very first telescope ever built that will be ready to really deal with, in a scientific way, how frequent everyday living is outside of the solar process,” claims Marc Postman of the Area Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md. “It could be zero % or 100 p.c or somewhere in in between. We really have no measurement at all.” The journey is in its infancy if it were to be imagined as a 100-meter race to start, we would be “putting on our sneakers,” Dressing claims. But the prize that awaits at the finish line is enrapturing, a cultural shift in our understanding of our put in the cosmos. “It could be a culture-shifting discovery,” Postman states.
HWO will usher in an age compared with any other, a person in which we actually know Earth’s position among the stars. The path forward, even so, is fraught with challenges, not minimum the enormous technological and political hurdles toward setting up these a equipment. Can we clear up them all to get our to start with glimpses of other dwelling worlds? The journey to find and examine alien Earths will span generations—but with their hottest meeting, HWO’s architects have now taken its most major first move.
Super-Hubble
If alien everyday living does exist, it has not created by itself effortlessly recognized. We have hunted for signals from intelligent civilizations, scoured the worlds of our solar method and tentatively probed some planetary atmospheres across interstellar gulfs, but a clear indicator of cosmic neighbors eludes us for now. To date astronomers have discovered additional than 5,500 worlds orbiting other stars. The bulk of these have tended to be worlds inhospitably weighty and very hot. The handful near to Earth in mass and sizing thrust the boundaries of plausibility for harboring everyday living as we know it they reside in restricted orbits around crimson dwarf stars a lot lesser than our sun. For a accurate exam of life’s cosmic prospective customers, we require to find and study planets eminently like Earth orbiting stars like our sunshine. “This has been percolating in the group for a pretty extended time,” Dressing states.
In 2021 the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Drugs instructed NASA to start out function on a device to obtain this objective as aspect of its decadal study, which offers the place company its marching orders every single 10 many years. The decadal study committee targeted on two proposed telescopes up to the task—one known as the Massive UV/Optical/IR Surveyor (LUVOIR) and the other, Habitable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx)—which its closing report put together into a one concept. The report instructed NASA to construct a telescope that could observe in infrared, optical and ultraviolet mild and “search for biosignatures from a strong amount of about 25 habitable-zone planets.” By the telescope’s optics, each world would be at best a lone, fragile dot of light—this is seemingly meager, but it would be plenty of to review the chemistry of the planets’ atmospheres for signs of life by using gases these types of as oxygen and methane at a full believed price of no more than $11 billion in 2020 pounds. Mark Clampin, the Astrophysics Division director at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C., later gave this hybrid telescope its latest title. “The a single title I imagined definitely captured the spirit of what we’re accomplishing is the Habitable Worlds Observatory,” Clampin claims. “This is the mandate we were specified.”
Construction of the telescope is years absent. In September 2023, even so, NASA picked a group of about 60 researchers to get started setting up a significant-amount “parts list” for HWO and its essential components. The groups, just one called the Science, Know-how, Architecture Critique Staff (Start off) and the other the Technological Assessment Team (TAG), are envisioned across the following year to hold formal community conferences every several months together with lesser-scale, more frequent intragroup conferences as properly as broader discussions with the wider astronomy neighborhood. “It’ll be a hectic yr,” claims Megan Ansdell, HWO’s application scientist at NASA Headquarters.
A 3-working day celebration in Washington, D.C., that commenced on Oct 31 was the to start with of these scheduling meetings—the setting up gun in the decadal-paced race to make HWO a fact. “I want to persuade you all to breathe…. Just breathe for a minute,” stated John O’Meara of the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii, co-chair of Start out, who aptly afterwards donned the Gandalf costume, on the very first working day of the assembly. “It took a long time to get here. It is heading to get a extensive time to go to the following stage…. We’re going to be doing work with each other for a very long time.” Though the overall quantity of the two virtual and in-human being attendees at the jubilant meeting numbered about 200, “it’s heading to take hundreds if not countless numbers of individuals to get this carried out ideal,” O’Meara stated. “I really do not know when this observatory is likely to launch. But I do know I promised my spouse I would retire when it does.”
A crucial topic of the setting up assembly was that in spite of HWO’s name, the observatory should really offer a lot more than glimpses of light-weight from putative mirror Earths. The immensity of the optics required to picture exo-Earth analogues would make HWO supremely useful for many other astronomical jobs, too—similar to its workhorse predecessors this kind of as NASA’s Hubble and the James Webb Room Telescope (JWST). “Studying darkish subject is a likelihood, the interstellar medium, galaxies—pretty much every factor of astrophysics,” states Lee Feinberg of NASA’s Goddard Room Flight Center in Maryland. “This will be a normal-course observatory.” Building that information very clear will be essential, mentioned Jane Rigby of NASA Goddard, JWST’s senior challenge scientist, in a converse on working day two of the conference. “We have a whole lot of perform to do,” she mentioned. “We really should halt contacting it ‘Habitable Worlds’ since that [name] tells the standard astrophysics community, ‘This is not for you.’” Postman describes it just: “This is definitely like a ‘super-Hubble,’” he states.
Pale Blue Dot
The vision of HWO coalescing in its planners’ heads seems like some thing between JWST and Hubble in design. The telescope’s most important mirror will likely be divided into honeycomblike segments—like that of JWST—allowing it to be folded up into a person of several massive new rockets below enhancement, these as SpaceX’s Starship or Blue Origin’s New Glenn. “We see segmented as the way to go,” Clampin claims. The mirror’s size—which drastically influences HWO’s final acuity—is as yet unfinalized but will at minimum amount match JWST’s 6.5 meters (21 ft) and could scale up to reach 9 meters (30 feet). Like JWST, the telescope might sport a vast deployable sunshield to block incoming light from our household star and will be stationed at a deep-place locale 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. In contrast to JWST, however, which probes deeply into the infrared to see the faint thermal glow of historic galaxies, HWO won’t involve extraordinary cryogenic cooling to carry out its observations. Instead of an unfurling sunshield, HWO’s mirror may perhaps be stored in a barrel-like tube, like Hubble’s. This shroud may possibly clear up a single of the most worrisome challenges confronted by JWST: micrometeorite strikes have dinged and dented its substantial exposed mirror. “A great deal of men and women are wondering that [shroud] appears to be like good,” claims Aki Roberge, associate director for technologies and method in astrophysics at NASA Goddard.
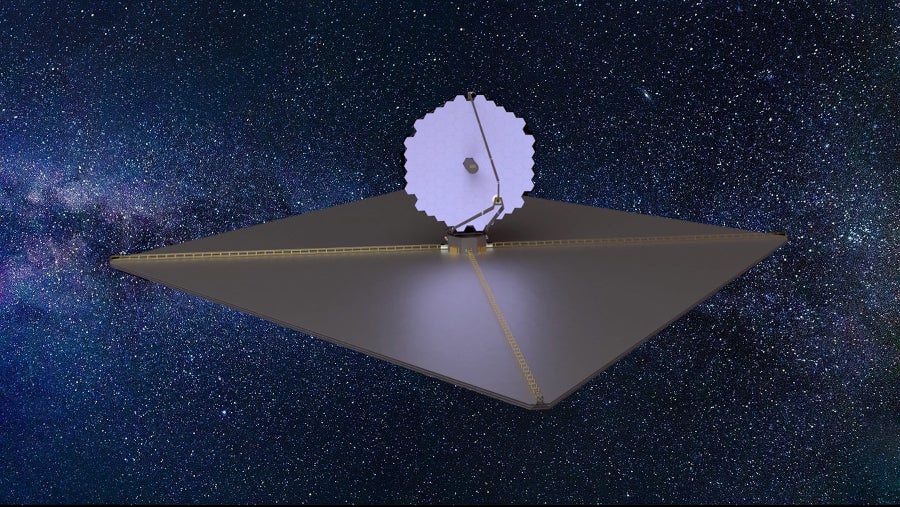
HWO’s best complex challenge—imaging an Earth-like planet—is really twofold: the telescope desires not only a technique to clear away the otherwise-overpowering glare of a planet’s star but also a way to maintain by itself breathlessly nevertheless to keep a specific planet in its sight. JWST was built to show a targeting drift as scant as one twentieth of a micrometer—a micrometer is a millionth of a meter and a portion of the width of a human hair. The telescope has exceeded those people abilities by a variable of 10, Feinberg states, meaning that it is steady to within a strand of human DNA. Unbelievably, HWO will continue to will need to be “maybe a factor of 1,000 improved,” he claims, with a stability of up to tens of picometers—a unit of measurement that is a trillionth of a meter, considerably less than the radius of a hydrogen atom. HWO will not need to continuously be so constant, but it will require to use this ultrastability method when it appears to be like at other Earths. A established of deformable optics—some of the telescope’s mirrors will be equipped to flex at any time so somewhat to eradicate any errors—will be a single of a number of very important equipment to accomplish the feat, HWO’s planners say.
To document a solitary photon of mirrored light-weight from an alien twin of Earth, HWO very first requires to filter out circa 10 billion photons from the planet’s sunlike star. A coronagraph—essentially a little precision-shaped disk in the telescope’s optics to include the star still enable planetary light to pass through—will probably be HWO’s primary way to attain this Herculean undertaking. HWO’s notional coronagraph would be constrained to a fairly tiny swath of wavelengths—tuned for optimum sensitivity to Earth-sized worlds orbiting in the habitable zone or “Goldilocks zone” of sunlike stars, the circumstellar location wherever temperatures may perhaps be neither too hot nor much too chilly for liquid water to exist. NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Room Telescope, established for start in 2027, will consist of a technological precursor for HWO’s coronagraph, albeit a single that boundaries Roman to imaging planets larger than Jupiter. The functionality of Roman’s coronagraph will present vital facts for HWO’s grander aspirations. “The coronagraph [on Roman] is a technology demonstration,” Dressing says. “For HWO it’s a vital instrument.”
Another way to suppress starlight would be to use a big, sunflower-formed “starshade” formation-traveling in area considerably forward of HWO’s gaze to solid a deep, earth-revealing shadow throughout its optics. But a independent spacecraft is a a lot far more sophisticated and unwieldy starlight-suppression solution than a coronagraph and so is not likely to be component of HWO from the get-go. Alternatively most experts see a starshade as a doable write-up-start add-on. “You can envision launching HWO with a coronagraph, accomplishing initial observations and then later on launching a starshade,” Dressing states. That would enable planets to be found further out from their stars and in far more detail than with a coronagraph on your own.
With either of these systems HWO really should be capable to supply photos of potentially habitable alien worlds akin to the well-known Pale Blue Dot picture of Earth taken by the departing Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1990 at the request of famed astronomer Carl Sagan. Exactly which devices HWO would concentrate on stays undecided. There are about 500 sunlike stars within 100 gentle-decades of Earth—which is about as considerably as HWO’s life-obtaining survey would seem probably to see. In January 2023 Eric Mamajek, deputy software main scientist of NASA’s Exoplanet Exploration Program in California, co-authored a listing of the most promising stars to notice in just this volume of area. “I suspect that most of the top rated 50 or so have a extremely significant likelihood of producing it to the ultimate survey list,” he says.
Settling on a goal record is complex by the point that only HWO could be capable to detect Earths in habitable zones all-around these stars, meaning that it would act as both surveyor and scrutinizer no other presently planned telescope comes wherever close to obtaining comparable abilities. This does increase the concern of no matter if sufficient targets can be found in the decades ahead to serve as HWO’s raison d’être, but for the time currently being most astronomers appear unconcerned. Proxy measurements can however winnow down HWO’s targets. “If there is a Jupiter right in the middle of the Goldilocks zone, you almost certainly don’t want to hassle on the lookout for an Earth there,” says Bruce Macintosh, director of College of California Observatories at the College of California, Santa Cruz. “But it is not truly that significant to mission achievements to know this star has an Earth and this 1 does not, since the very best Earth detector will be the mission we’re building”—HWO.
Renaissance
Problems in excess of the place, precisely, to level the telescope are element of what might be the project’s major challenge of all: making certain unflagging support for the many years necessary to see it by way of, both equally from the public and from Congress, which will finally source HWO with funding. “We will need champions at [NASA] Headquarters, in Congress, in public and in sector so that when things are going difficult, they’re chatting on our behalf,” explained Matthew Bolcar of NASA Goddard in a chat on working day two of the HWO setting up conference. Greatly talked over were being lessons to be realized from JWST, which was plagued by embarrassing and perhaps ruinous spending plan overruns and timetable slips. In an hard work to steer clear of those people very same blunders, HWO is the crown jewel of a new NASA software known as the Great Observatory Mission and Technology Maturation Method (GOMAP), which will thoroughly manage the finances and progress of the agency’s upcoming big house telescope jobs.
JWST’s ultimate good results in spite of its setbacks, having said that, may be trigger for optimism. “In the 10 years in advance of we introduced…. I can not rely how lots of people today had been like, ‘This thing’s never ever likely to get the job done,’” Rigby claimed in her talk but, she said, the observatory’s above-expectations overall performance displays that “this is a doable point.” And, several of HWO’s planners eagerly take note, it will have a significant edge around JWST in that it will be built from the begin to be serviceable, just like Hubble. This signifies robots or astronauts could go to the telescope to periodically give it new leases on existence, earning repairs and swapping out devices “sort of IKEA-type,” Roberge suggests.
If the know-how and science powering HWO can be finalized, funding for the telescope can be secured and support for the venture can be preserved, the payoff is nearly unfathomable. In its examine of some two dozen Earths in our corner of the galaxy, HWO will convey to us if any of these worlds could aid existence or perhaps nevertheless do now. In the most wildly optimistic scenarios it could even see indications of technological civilizations, these types of as the evening lights from notional alien metropolises or obvious indicators of industrial air pollution in an alien atmosphere. “You may possibly use this telescope to search for ‘technosignatures’—evidence for not just straightforward life like micro organism but sophisticated lifetime able of developing devices, sector, electric ability, all of that,” Postman says. These types of a chance may possibly appear to be considerably-fetched but remains at the edge of technical feasibility—and the risk of achievements in these kinds of queries will without end keep on being zero if they are never carried out.
On the other hand, HWO may possibly scrutinize its targets and uncover none to comprise something we understand as a indicator of life, primitive or if not. These kinds of an end result would be disappointing but no a lot less valuable. It would be the ideal proof however that Earth really is unique in a cosmic sense—a treasured oasis in a seemingly lifeless pocket of the Milky Way. “You would have a superior higher restrict on how exceptional lifestyle is right now,” Postman suggests. A strong detection of a residing planet, Dressing speculates, could drastically alter our very tradition, spurring a “whole new renaissance of art and literature”—not to point out even larger investments in much more considerably-viewing area telescopes. Conversely, a failure to come across anything at all may feel depressing but would not genuinely be a “failure” at all—we people would the moment again come across ourselves seemingly solitary atop some cosmic pinnacle in a location of profound privilege we’d do perfectly to improved nurture and respect. “Either of those people results would be extremely attention-grabbing from the two a scientific and philosophical level of check out,” Postman states. We are lacing up our footwear at the start off of that race to the best prize. A podium of unbeatable know-how awaits.
[ad_2]
Resource backlink