[ad_1]
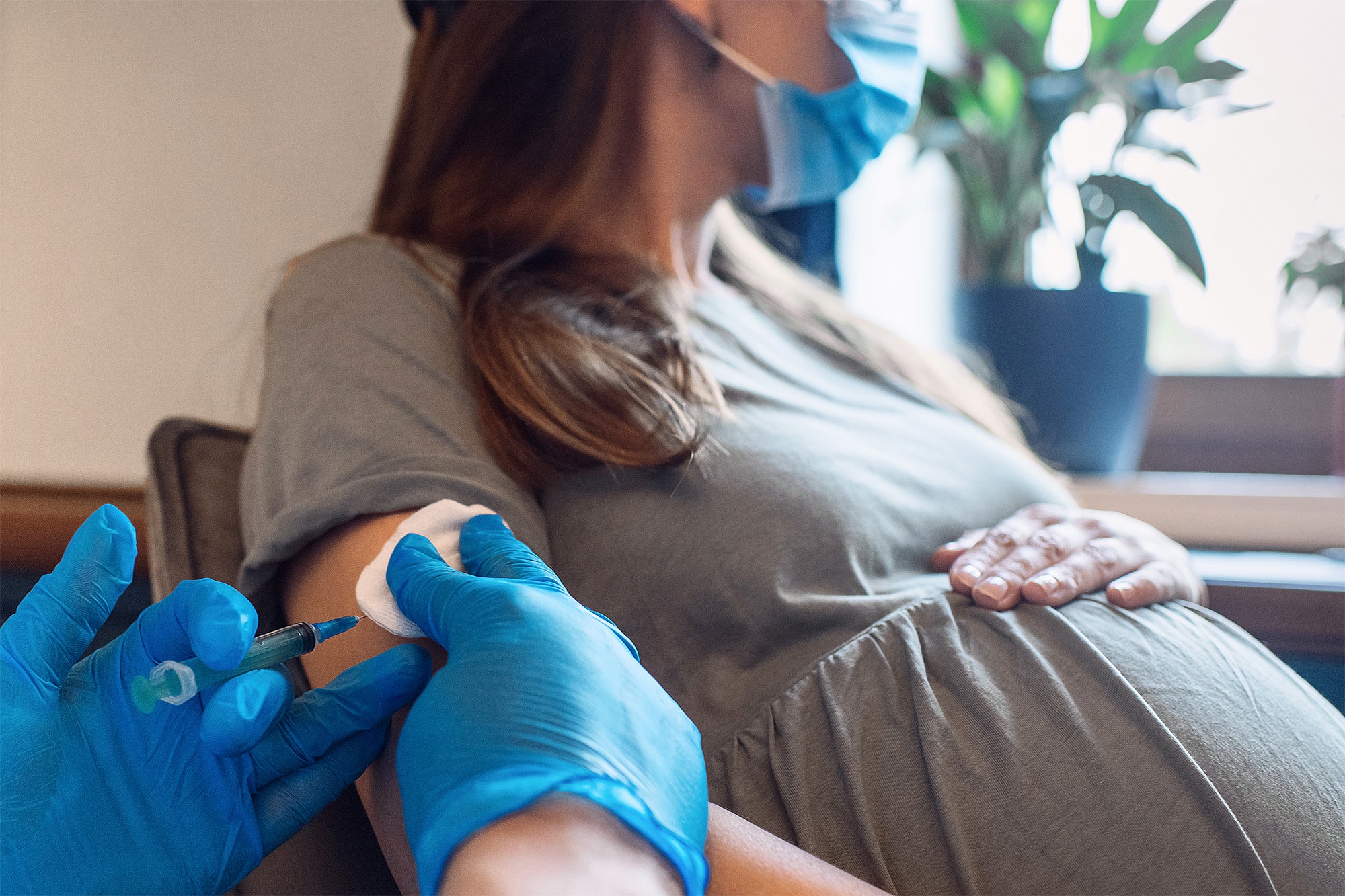
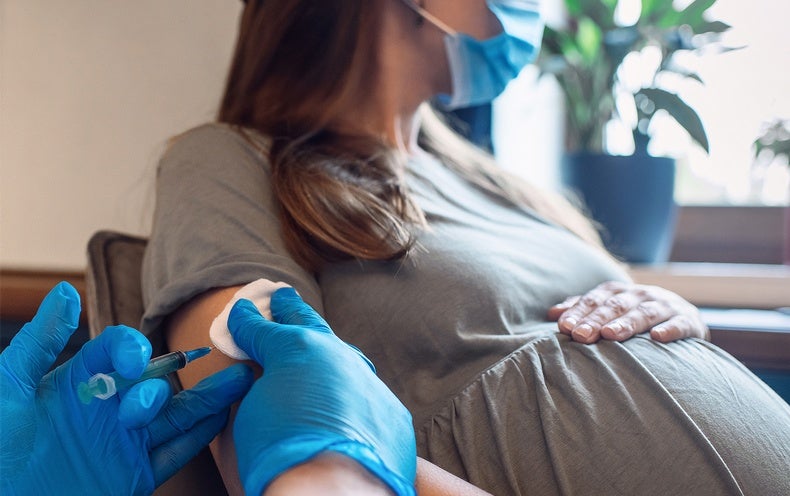
When the U.S. Foodstuff and Drug Administration permitted the most modern respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine on August 21, it turned the first vaccine that experienced been formulated specially to be provided during pregnancy to shield the toddler soon after delivery to get the go-ahead. But it’s not the initially vaccine that the Centers for Sickness Manage and Avoidance has encouraged for the duration of being pregnant. It joins pictures for influenza, Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis) and COVID—and is element of a system of immunizing folks all through pregnancy that has attained steam and amassed supporting proof in the past two many years.
Expectant people today will have a alternative of how to guard their new child against RSV. They can opt to get the new parental RSV vaccine concerning 32 and 36 months of pregnancy—which will prompt their immune method to develop antibodies in opposition to RSV that will cross the placenta to the fetus and thereby protect the newborn by passive immunity for at minimum 6 months. Or they can wait around until finally just after their toddler is born and give them nirsevimab, a monoclonal antibody that was authorized by the Fda in July, which also provides passive immunity ahead of RSV season.
But the possibility of a pregnancy vaccine for RSV could be additional hassle-free if a person is currently finding vaccinated versus flu, COVID and pertussis in the course of prenatal visits. And the new vaccine additional solidifies the escalating acceptance of utilizing immunization throughout pregnancy to defend newborns towards health conditions at an age when their immune technique is not mature ample to mount its personal defense.
“The neonatal immune program is comparatively immature, and it usually takes time to develop immunity to pathogens, either by way of vaccination—because various doses are desired to attain protection—or via all-natural exposure,” suggests Catherine Mary Healy, an associate professor of pediatrics at Baylor College or university of Medication and Texas Children’s Medical center. “And at times the infection can strike ahead of [childhood] vaccination.”
Numerous infections materialize right about the time of delivery, ahead of most vaccines are given, claims Kathryn Edwards, a professor of pediatrics and scientific director of Vanderbilt University’s Vaccine Investigation System. “But when you immunize the mom, you guard the mom from a ailment that she could existing to the toddler, and you safeguard the infant from condition. So it is a twofer—one shot but with the defense of two.”
A Heritage of Additional Warning
It took a rocky 50 percent-century of study to bring the RSV vaccine to fruition, but it’s taken more than twice as prolonged for pregnancy vaccines to develop into extensively acknowledged by the community and by scientists and clinicians.
“As much back again as the 1800s, it was understood that mothers who survived vaccinia infection gave delivery to infants who were being a lot less most likely to become contaminated,” states Healy, referring to the virus utilized in the smallpox vaccine. A couple of little trials in the 1930s and 1940s showed that vaccinating expecting men and women versus pertussis prevented their infants from acquiring it for the initial quite a few months following birth, and a 1961 trial discovered that vaccination through pregnancy protected newborns from neonatal tetanus.
“For a lengthy time, we were being afraid to vaccinate expecting individuals, and extra importantly, we have been terrified to do trials in expecting people because we see them as a shielded class of people today who are vulnerable,” claims Kawsar Talaat, an affiliate professor of intercontinental well being at Johns Hopkins University. But that perspective has been changing as a lot more investigate has proven the danger of specific bacterial infections in the course of being pregnant and the security and performance of vaccination. “There’s been a massive shift, possibly in the previous 15 a long time, in vaccinating expecting people—not just for their safety but also for the protection of their fetuses and subsequent newborns,” Talaat suggests.
Neonatal tetanus, for illustration, killed an estimated 787,000 newborns globally in 1988. Even though improving hygienic tactics all through delivery can minimize a part of those deaths, only tetanus vaccination all through being pregnant eradicates the danger, so the Earth Well being Corporation made tetanus vaccination all through being pregnant a best precedence in 1989.
Wellness professionals have known considering that at the very least the 1918 flu pandemic that results from flu are worse during being pregnant, each for pregnant people today and for their chance of miscarriage and preterm birth. In the 1957 flu pandemic, influenza was the top trigger of death for the duration of pregnancy. But while the U.S. Surgeon Basic first proposed flu vaccination through pregnancy in 1960, the press to vaccinate expecting people today in opposition to flu did not really choose off till the menace turned specifically apparent—especially to the normal public—during the 2009–2010 H1N1 swine flu pandemic.
“What we’ve learned above time is that if you are a pregnant individual and you deal influenza, you are about two to 3 occasions a lot more probable to be hospitalized and die than a man or woman of the exact same age who is not pregnant,” states Paul Offit, an infectious condition medical professional and director of the Vaccine Education Centre at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “So as these facts grew to become clearer, it turned considerably extra persuasive to give an influenza vaccine in the course of pregnancy.” Expanding proof has demonstrated that flu vaccination all through being pregnant also decreases the threat of miscarriage and preterm birth although guarding newborns right up until they can get their very own flu vaccine at 6 months aged.
The Tdap vaccine was next to be part of the roster of advisable shots during being pregnant. Pertussis premiums commenced climbing in the 2000s as evidence unveiled that protection from an up to date pertussis vaccine given through early childhood wore off sooner than expected. So in 2012 the CDC began recommending that expecting folks get a Tdap vaccine concerning 27 and 36 months of gestation so that their antibodies would transfer to the fetus and secure the newborn.
Then in late 2019 a new virus arrived that threatens both pregnant individuals and their fetuses. “With COVID, we saw all over again that being pregnant was a sizeable chance and that individuals who ended up expecting had been a lot additional likely to conclude up in the medical center and [die], with improved chance of fetal reduction and miscarriage,” Talaat suggests. Once more, however, businesses have been hesitant to conduct COVID vaccine trials with pregnant volunteers, which still left pregnant individuals susceptible to infection, she states.
“When the COVID vaccines were unveiled in December of 2020, the CDC essentially reported that a expecting person could reasonably pick out to get this vaccine due to the fact they understood that you were a lot more very likely to be hospitalized and die [from the disease],” Offit says. Then the V-safe and sound method and Vaccine Basic safety Datalink—two vaccine security surveillance programs utilized to look for adverse events from COVID vaccines—revealed no important dangers to vaccinating expecting folks, “and it became an urgent advice,” he says.
In spite of today’s greater acceptance of pregnancy vaccines, conducting clinical trials with pregnant volunteers stays fraught. “When individuals think about irrespective of whether to immunize by themselves throughout being pregnant, what they have top of thoughts is, ‘Could this potentially harm my newborn?’ It is a sensible worry,” Offit states.
In an era of vaccine hesitancy and enhanced litigation, pharmaceutical providers may possibly experience the require to be further careful about even the physical appearance of a basic safety problem. GSK stopped its have demo of an RSV vaccine for expecting individuals in February 2022 since infants born in the vaccine team had been a lot more possible to be born preterm. Among 5,235 toddlers born to individuals throughout the GSK trial, 6.8 p.c in the vaccine group have been preterm, which is a statistically considerable variance in comparison with virtually 5. per cent of toddlers born prematurely in the placebo team.
But the enhanced possibility of prematurity happened only in minimal- and middle-earnings nations, and the obtaining was only considerable when in comparison with infants born to moms who did not acquire the flu or COVID vaccines. It is plausible that the RSV vaccine did not improve the chance of prematurity but somewhat that the flu and COVID vaccines lessened that chance, Offit claims. All those calculations ended up hardly ever carried out since GSK scrapped the demo, even so.
More Vaccines on the Horizon
Researchers are forging in advance with other potential pregnancy vaccine candidates. “I do see this new wave of fascination in parental vaccines adhering to on the heels of the RSV vaccine accomplishment and the pertussis vaccine accomplishment,” says Sallie Permar, chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Healthcare School. But it is far more than just observing the performance of individuals vaccines, she adds.
“Honestly, I think it’s also from much more females acquiring into management positions in areas like [pharmaceutical companies] that are tipping the scales and also that as just about every pandemic will come out, it nearly invariably has much more critical effects on pregnant people and fetuses,” Permar states. “Other areas of the populace are commencing to notice that vaccines are highly desired for that inhabitants, so there’s a greater willingness to do trials for the duration of pregnancy,” she claims.
Permar has been performing to produce a vaccine from cytomegalovirus (CMV), the main infectious induce of start flaws. A CMV an infection for the duration of pregnancy, even in someone who has presently had CMV, can result in really serious complications for the fetus. These incorporate developmental delays, seizures and vision or listening to reduction.
Perhaps the most significant future contender for a pregnancy vaccine is a single towards group B Streptococcus, a type of micro organism that can move to the fetus for the duration of labor and childbirth and induce existence-threatening an infection, which include meningitis, pneumonia or sepsis. Offering a pregnant individual antibiotics in the course of labor can reduce an infection through a newborn’s 1st week of life—but it simply cannot secure against late-onset bacterial infections, which can arise involving just one 7 days and 1 month following delivery.
“We appear to be to have arrive as much as we can in stopping [early-onset disease], and the needle hasn’t moved at all in conditions of late-onset sickness,” Healy suggests. Vaccination for the duration of being pregnant appears to be like the most evident way to lengthen that safety, she adds. One particular promising GBS vaccine prospect is at this time in section 2 trials.
Of program, vaccines only operate when individuals get them. Whilst both of those the flu and pertussis vaccines have been advised throughout pregnancy for far more than a decade, only all over fifty percent of expecting men and women in the U.S. really get both vaccine. Experiments advise amongst 60 and 70 per cent of pregnant men and women acquired the COVID vaccine previous calendar year.
Irrespective of whether expecting men and women will pick out to get the RSV vaccine remains to be seen. “It may well be that the negative RSV time we skilled last yr assists transfer the needle towards acceptance,” Healy says. “Studies exhibit that a strong company suggestion is the most important issue in influencing a person’s vaccination selection, even if vaccine-hesitant.”
[ad_2]
Supply url