[ad_1]
An increasing quantity of researchers is turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor biodiversity and bolster initiatives to support endangered species. Not like common solutions that can disrupt ecosystems or have to have sizeable time, labour and assets, AI has the potential to rapidly and properly analyse vast quantities of authentic-globe info.
“Without AI, we’re never going to accomplish the UN’s targets for preserving endangered species,” says Carl Chalmers, who reports device learning at Conservation AI, a Uk-primarily based non-earnings organization in Liverpool that works by using AI technological innovation for several ecology initiatives.
Species are vanishing at a price hundreds to thousands of moments more rapidly than that tens of millions of yrs in the past, with up to 1 million species on the brink of extinction. In response, the United Nations established a intention in 2020 to safeguard at least 30% of Earth’s land and oceans by the stop of the 10 years.
AI is “imperfect” but could accelerate crucial discoveries, states Nicolas Miailhe, Paris-based mostly founder of The Future Modern society, an worldwide non-financial gain organization that aims to much better govern AI. “We really much need human practitioners in the loop to design and style models, as very well as acquire, label, quality check out and interpret data,” he states.
Soundscape evaluation
Ecologist Jörg Müller at the University of Würzburg, Germany, and his colleagues have revealed that AI instruments can assistance to quantify biodiversity in tropical forests by figuring out animal species from audio recordings.
In a research revealed on 17 October in Mother nature Communications, the researchers made use of AI to analyse animal ‘soundscapes’ in the Chocó, a area in Ecuador regarded for its abundant species variety. They put recorders in 43 plots of land symbolizing unique levels of restoration: forests that ended up untouched by deforestation, locations that experienced been cleared but then abandoned and had started out to regrow, and deforested land actively made use of for cacao plantations and pasture. They gave the audio files to authorities, who had been capable to determine 183 fowl, 41 amphibian and 3 mammalian species.
The scientists also fed their recordings to a form of AI design identified as a convolutional neural network (CNN), which experienced now been created to identify fowl appears. The CNN was ready to decide on out 75 of the chicken species that the professionals experienced, but the model’s information established was limited and contained only 77 chicken species that could take place in the area. “Our outcomes exhibit that AI is prepared for more thorough species identification in the tropics from audio,” suggests Müller. “All that is essential now is a lot more education knowledge gathered by human beings.”
The workforce suggests that using AI to precisely evaluate the biodiversity of regenerated forests could be very important for analyzing biodiversity projects that should exhibit good results to protected continued funding.
Camera-lure footage
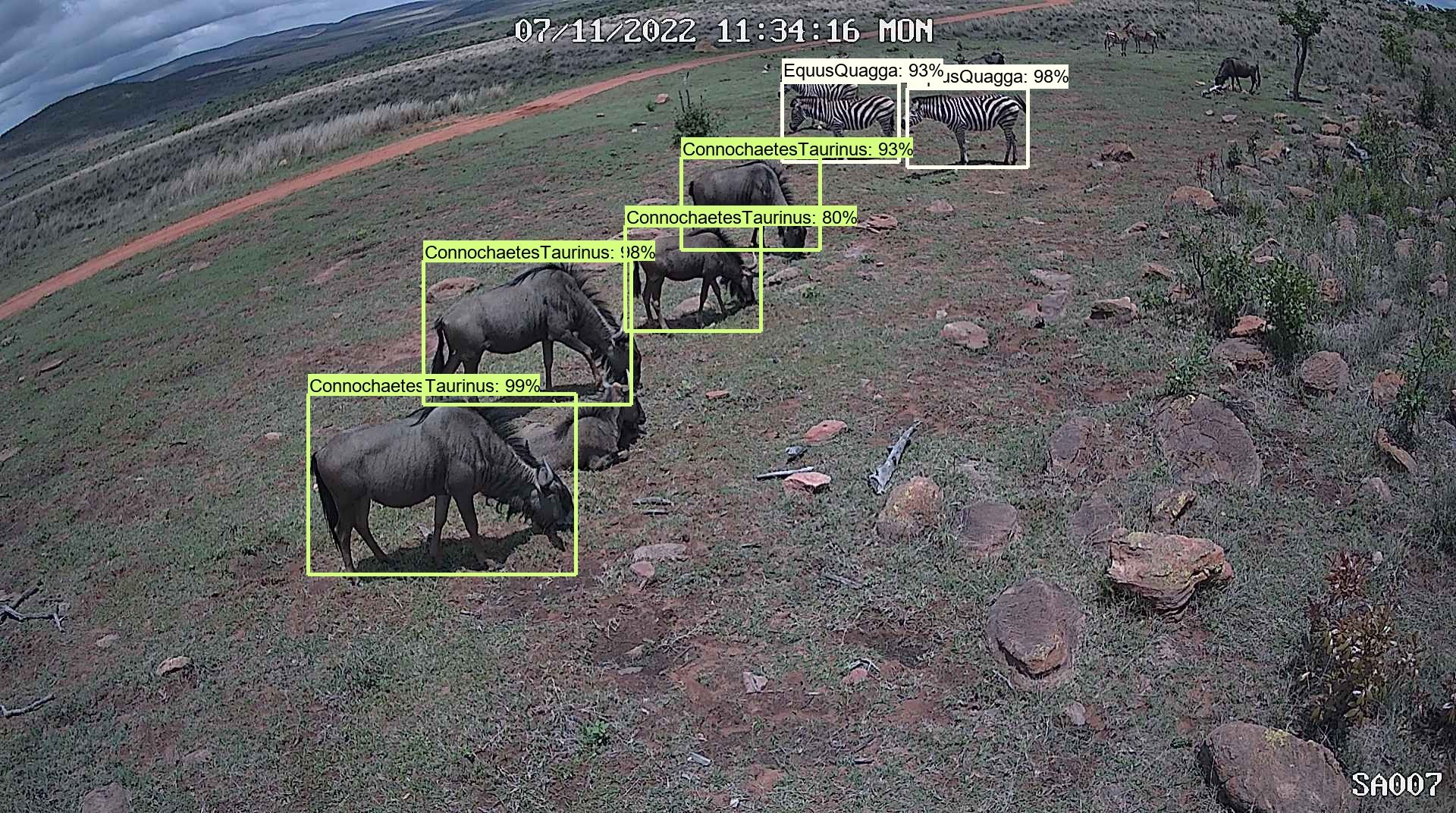
Scientists at Conservation AI have produced models that can scour via footage and photographs from drones or camera traps to discover wildlife — which include critically endangered species — and keep track of animal actions.
They constructed a totally free on-line system that takes advantage of the technologies to quickly analyse photographs, online video or audio files, like data from authentic-time digicam-entice footage and other sensors that authorised users can add. End users have the option to be notified by e-mail when a species of curiosity has been noticed in the footage they have uploaded.
So much, Conservation AI has processed more than 12.5 million illustrations or photos and detected much more than 4 million particular person animal appearances across 68 species, which includes endangered pangolins in Uganda, gorillas in Gabon and orangutans in Malaysia. “The platform can process tens of 1000’s of illustrations or photos an hour, in distinction to individuals who can do a several thousand at greatest,” states Paul Fergus, one of Conservation AI’s lead researchers. “The speed at which AI processes data could permit conservationists to defend vulnerable species from sudden threats — these types of as poaching and fires — rapidly,” he provides. Conservation AI has currently caught a pangolin poacher in the act by analysing footage in genuine time.

As perfectly as monitoring biodiversity in genuine time, AI can be employed to design the impacts of human things to do on an ecosystem and reconstruct historic improvements. Scientists have used AI to find out how a century’s value of environmental degradation in a freshwater ecosystem has led to biodiversity reduction.
Although it is properly documented that human things to do have resulted in biodiversity decline in rivers and lakes, little is recognised about which environmental components have the major impact. “Long-time period facts is pivotal to connection alterations in biodiversity to environmental adjust and to outline achievable conservation goals,” says Luisa Orsini, who studies evolutionary biosystems at the University of Birmingham, Uk.
Orsini and her colleagues created a product that backlinks biodiversity to historic environmental variations employing AI. In a examine revealed in eLife earlier this yr, the team acquired genetic materials that had been left guiding more than the previous century by vegetation, animals and micro organism in the sediment of a lake. The sediment levels have been dated and environmental DNA was extracted for sequencing.
The researchers then mixed these info with local weather info from a temperature station and chemical-air pollution knowledge from direct measurements and nationwide surveys, using an AI built to cope with varied forms of information. Orsini suggests the aim was to establish correlations among the the ‘mayhem’ of data.
They observed that the presence of insecticides and fungicides, together with extreme-temperature functions and precipitation, could describe up to 90% of the biodiversity loss in the lake. “Learning from the past, we showcased the price of AI-based mostly approaches for knowledge previous drivers of biodiversity decline,” claims review co-author Jiarui Zhou, who is also at the University of Birmingham.
The major benefit of utilizing AI is that it is speculation cost-free and knowledge pushed, suggests Orsini. “AI ‘learns’ from earlier information and predicts potential traits in biodiversity with bigger precision than at any time achieved ahead of.”
Miailhe is hopeful that AI can be routinely used to true-planet conservation endeavours in the in the vicinity of potential. “That’s clearly the way to go,” he states. But he warns that AI consumes computing power and material methods, which finally has adverse effects on ecosystems. “Environmental impression assessments need to be at the centre of AI possibility administration,” he suggests.
This write-up is reproduced with authorization and was very first released on October 27, 2023.
[ad_2]
Source url



