[ad_1]
Researchers have recognized a person with a unusual genetic mutation that shielded him from producing dementia at an early age. The discovering, printed on 15 May well in Character Medication, could assist scientists to improved recognize the causes of Alzheimer’s disorder and possibly guide to new treatments.
For virtually 40 decades, neurologist Francisco Lopera at the College of Antioquia in Medellín, Colombia, has been subsequent an extended spouse and children whose customers produce Alzheimer’s in their forties or before. A lot of of the approximately 6,000 family customers carry a genetic variant identified as the paisa mutation that inevitably potential customers to early-onset dementia. But now, Lopera and his collaborators have identified a family member with a second genetic mutation — one that shielded him from dementia till age 67.
“Reading that paper designed the hair on my arms stand up,” claims neuroscientist Catherine Kaczorowski at the College of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “It’s just this sort of an important new avenue to pursue new therapies for Alzheimer’s illness.”
Mutated protein
Lopera and his colleagues analysed the genomes and clinical histories of 1,200 Colombians with the paisa mutation, which triggers dementia around ages 45—50. They determined the man with the next mutation when he was 67 and had only moderate cognitive impairment.
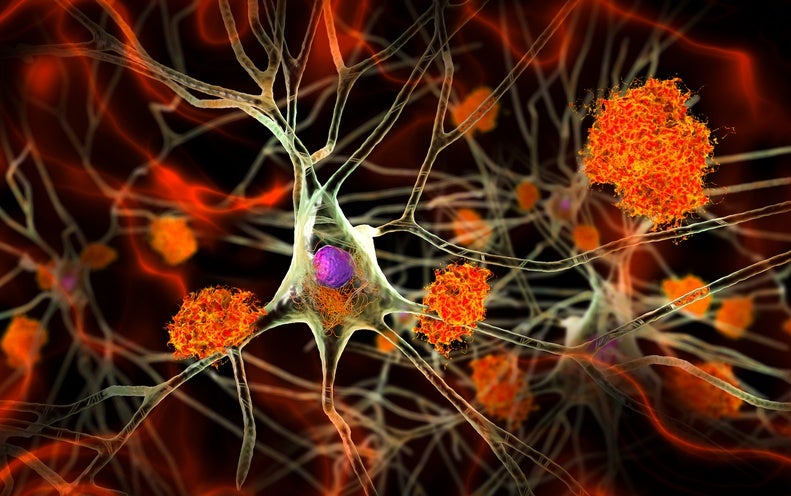
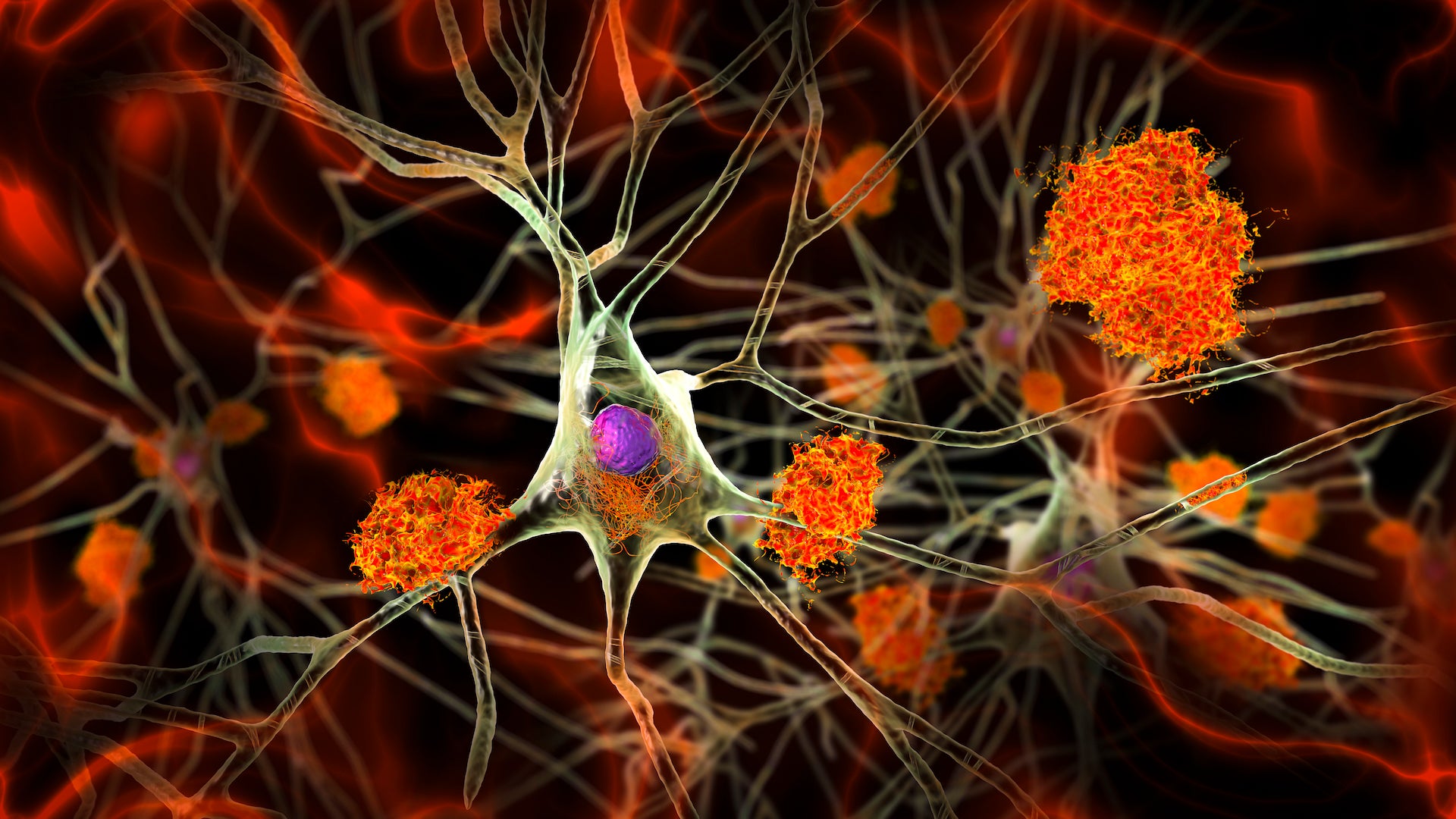
When the researchers scanned his brain, they uncovered significant concentrations of the sticky protein complexes identified as amyloid plaques, which are believed to get rid of neurons and induce dementia, as effectively as a protein termed tau that accumulates as the disorder progresses. The mind looked like that of a human being with significant dementia, claims research co-author Joseph Arboleda, an ophthalmologist at Harvard Health care University in Boston. But just one small mind space identified as the entorhinal cortex, which coordinates skills these as memory and navigation, had lower amounts of tau.
The researchers discovered that the gentleman had a mutation in a gene coding for a protein known as reelin, which is linked with mind diseases which includes schizophrenia and autism. Little is recognized about reelin’s purpose in Alzheimer’s, so the researchers genetically engineered mice with the identical mutation. In mice, the mutated kind of reelin prompted the tau protein to be chemically modified, restricting its capability to cluster all over neurons.
The examine troubles the theory that Alzheimer’s condition is mainly driven by amyloid plaques, which are the targets of a number of medication just lately authorised by the US Food and Drug Administration. The medication successfully take away amyloid from the brain, but direct to only a reasonable enhancement in costs of cognitive decline.
The point that the gentleman stayed mentally healthy for so extended regardless of the many amyloid plaques in his brain suggests that Alzheimer’s is extra intricate, claims Yadong Huang, a neurologist at the Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, California. He implies that there could be multiple subtypes of Alzheimer’s, only some of which are pushed by amyloid. “We do need unique pathways to seriously eventually deal with this sickness,” he claims. The website link to tau, he says, is specifically promising simply because it indicates that tau plays a position in psychological decrease. Several therapies targeting tau are at this time in clinical trials.
Shared mechanisms
Lopera suggests that the reelin mutation is particularly exceptional in the standard inhabitants, but that his workforce is now searching for this and other mutations among the people with the paisa mutation. The man’s sister, who experienced each the paisa and reelin mutations, began building cognitive impairment at age 58 and severe dementia at 64 — later on than common for someone with the paisa mutation. The authors say that she experienced knowledgeable head injuries and had other problems that could have contributed to her producing dementia previously than her brother.
Arboleda notes that the mutated reelin protein binds to the exact same receptors as a protein identified as APOE, which is also connected with Alzheimer’s ailment in persons who do not have the paisa mutation. In 2019, the exact same team experienced recognized a lady with the paisa mutation who designed dementia 30 decades later on than typical, owing to a mutation in APOE. Like the male in the most current review, the woman’s mind contained a great deal increased ranges of amyloid than would be envisioned in somebody with so few Alzheimer’s signs.
“It’s truly interesting because it’s telling us there’s some shared mechanisms,” Kaczorowski claims. Reelin and APOE compete to bind to the receptor, and the two results recommend that both a stronger reelin protein or a weaker APOE protein can shield the mind against the illness. Arboleda says this implies that therapies targeting reelin or APOE could possibly be even far more efficient in sporadic Alzheimer’s circumstances, which tend to be less intense and development extra slowly but surely than the early-onset form that the Colombian relatives experiences.
As with many individuals with Alzheimer’s, the man’s hippocampus — a brain area controlling learning and memory — was more compact than typical at the time of his demise, suggesting that it was degenerating. But for the reason that his cognitive talents remained somewhat intact, Kaczorowski says, neurons in other parts of the brain may have repurposed on their own to make up for the hurt. Being aware of whether that comes about, she provides, could assist to inform upcoming therapeutic techniques.
“The large majority of investigate focuses on why some people today have Alzheimer’s, extremely handful of are on conditions where by a aspect can go towards this condition,” states Huang. He suggests that even more research is necessary to pin down the mechanism by means of which reelin and APOE affect tau, and no matter if focusing on these proteins could help men and women with Alzheimer’s who do not have the paisa mutation. “This is a single of those couple instances that seriously opens the door for anti-Alzheimer’s study.”
This posting is reproduced with permission and was to start with published on May well 15, 2023.
[ad_2]
Supply url