[ad_1]
NASA has a planet-sized challenge on its fingers.
Ironically, the source of this is here on Earth: Congress, which has the penny-smart but pound-foolish plan of trickling out space company funding every single year, hobbling lots of of NASA’s mission targets that have to have wondering past the common two-year Home or 6-12 months Senate time period. This has repercussions that can be felt across the solar process.
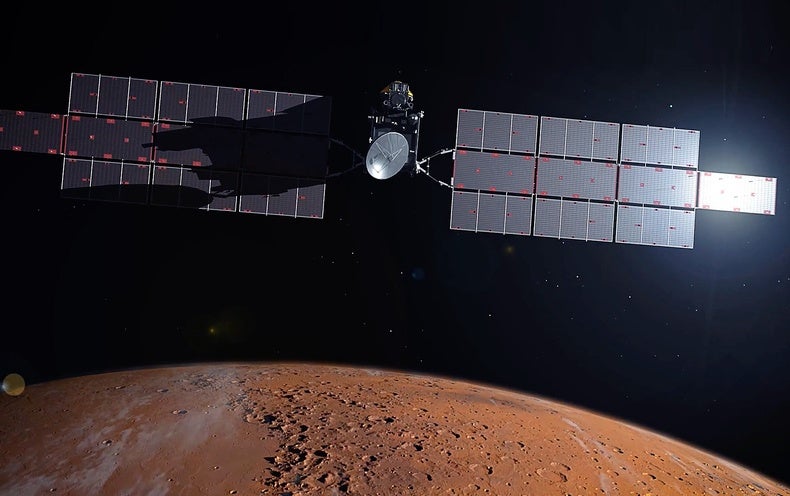
Proper now on Mars, the Perseverance rover is accumulating modest samples of the Purple Planet, gathered from within the 45-kilometer-broad Jezero crater that after held a massive lake, billions of decades back. Scientists contemplate it a person of the finest destinations to scout for proof of historical daily life on Mars, or at the very least see if situations had been ripe for its genesis.
These Martian souvenirs properly relaxation inside of hermetically sealed cylinders, both saved on board or dropped in strategic locations. A potential Mars-bound mission will decide them up and provide them to Earth for study.
The trouble? That return mission at present does not exist.
And it is not crystal clear when it will, either. In September, an independent assessment board investigated the recent condition of a Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission, and found there’s a “near-zero probability”—tech-converse for “no way”—for it to be prepared for start by 2028. It could satisfy a 2030 deadline, but at a price tag of $10 billion, which would make it among the most high priced science initiatives NASA has at any time carried out.
But it is a critical component of NASA’s plans.
The 2011 Nationwide Study Council’s Planetary Science Decadal Survey, created by a panel of dozens of major researchers, said that MSR is a “highest-precedence flagship mission” for the 2013–2022 10 years. An before 2008 NASA preliminary planning document claimed that of 55 significant investigations into Mars, half would be addressed by MSR. It is not challenging to see that looking into the strategy of lifetime on Mars, historic or extant, would be a critical scientific purpose for NASA, and just one with a potentially enormous affect on all humanity.
The 1st section is already underway. A 10 years-aged Mars 2020 Science Definition Group report said that applying the Perseverance rover to collect samples from the planet’s surface area would reduce the charge of a foreseeable future MSR mission. “Any variation of a 2020 rover mission that does not prepare a returnable cache would critically delay any substantial progress towards sample return,” it mentioned. Heeding that suggestions, Perseverance was built to accumulate individuals samples and has been performing so given that 2021. Now arrives the tricky(er) element: returning them to experts on Earth.
Until extremely not long ago, the plan was to use Perseverance alone to provide the gathered samples to a ideal landing place. Though this would take time away from its exploration (and, extra worrisome, would operate up versus the anticipated existence span of the rover) it is probably the most secure and best approach. Absolutely, the most expense-successful.
In the meantime, NASA would construct a lander and a Mars Ascent Motor vehicle (MAV), a rocket that would acquire Perseverance’s samples into Martian orbit (The lander would occur equipped with two sample-carrying helicopters primarily based on the effective Mars Ingenuity ‘copter as a backup if Perseverance couldn’t comprehensive the process). From there, a European Space Agency Earth Return Orbiter mission would rendezvous with the MAV, ingest the sample container—literally opening and “swallowing” it—and then bring it to Earth, exactly where it would land in the Utah desert like the current OSIRIS-REx asteroid Sample Return Capsule.
Nevertheless, the 2023 impartial review board put the kibosh on that, getting that this mission simply cannot be achieved in the necessary time frame for the offered price range.
In essence, NASA has to start off all above all over again scheduling MSR. The great news is that perform on this has currently begun, and the space agency hopes to have a new mission concept early following yr.
It’s simple to stage fingers at NASA for the value overruns and routine delays, but to be reasonable, the agency performed by all the administrative policies. That’s not to downplay mismanagement concerns, which the unbiased assessment report pointed out in element, but which, honestly, can be anticipated for enormous assignments throughout numerous divisions in a govt company. Committees achieved, suggestions were debated, reviewers reviewed, and the best plans innovative. Then actuality intruded. Obtaining to Mars is tough. A lot of missions never make it. Adding the very complicated specialized issues of not only having again, but accomplishing so after a complicated orbital rendezvous, tends to make matters a lot more than twice as really hard. Just acquiring from the Martian surface to orbit is ridiculously tough, and the significant NASA requirements for testing and redundancy—in the circumstance of the MAV, at least—make it all but impossible under the existing approach.
Where does this leave the mission? Nicely, MSR could be canceled, but that is evidently the worst feasible alternative. Given its worth scientifically—and, with all the time and cash now invested, as perfectly as the initiatives carried out by Perseverance—this isn’t some thing to be regarded realistically. NASA could trim MSR’s price range, slicing charges, but at this issue undertaking so in the existing approach would do a lot more hurt than fantastic. There is no science getting carried out with MSR, so all the engineering is geared toward finding up the samples and having them to Earth reducing any of the tech essential to do that could jeopardize the mission.
So here’s my radical imagined: Fund it. Thoroughly. Give NASA what it demands to make this mission operate, which include a broad enough margin for complex safety offered the hard nature of the engineering and administration.
By funding it, I never necessarily mean robbing Peter to spend Paul as has transpired to other NASA missions that ran in excess of spending plan, using necessary funds absent from other deserving area agency endeavors. I also don’t believe merely producing it a independent line item in NASA’s price range, as was carried out with the James Webb Place Telescope when its expenses bloated, will get the job done both. It may possibly suffice for this distinct case, but it is not a very long-term option for NASA’s targets.
The simple problem right here is that NASA’s funding is a zero-sum game, so charge overruns in a single mission will automatically effect other individuals. But that sport of shuffling money would not be so dire if NASA pretty simply just experienced a greater total spending plan. This would also fix many of the management complications pointed out in the 2023 MSR report, making it possible for NASA to hire far more technical and administrative staff members for the task.
This really should not be controversial. Public perception of NASA’s funding is massively exaggerated above its true spending plan in one particular 2018 poll the regular American assumed NASA acquired in excess of 6 percent of federal shelling out, when in truth NASA receives only fifty percent a per cent. Presented the wonderful achievements NASA accomplishes with this very small slice, a dedicated work to accurate this false impression would make the political struggle of increasing the room agency’s funding significantly much easier.
From a strictly economic level of check out, NASA returns much more funds than is provided. The agency has estimated that it generated economic output of $71.2 billion in 2021 that places its return on financial investment at a little something close to $3 for just about every greenback put into it. And, of program, we get considerably extra from NASA than simply just economic rewards.
We never commit money on NASA we spend it.
 

In typical, NASA’s science and exploration enjoys wide bipartisan support. This is particularly exceptional in today’s political local climate, where it could possibly be difficult to get the two functions to agree on the time of working day, and the place the Republicans have a history of trenchant antiscience stances—especially when it arrives to climate, a area of science NASA closely supports.
Expanding NASA’s budget need to be a no-brainer. Alternatively, although, Congress has a historical past of targeting NASA whenever a budgetary ax is wielded. This makes zero feeling presented how small a portion the agency receives the volume of revenue the Division of Defense wastes each and every calendar year is equivalent to NASA’s complete once-a-year budget. Cutting NASA’s finances is like creating place on a computer’s tough generate by deleting small textual content data files even though disregarding the gigabyte videos you’ve presently viewed.
Make sure you be aware I’m talking about what we ought to do—that is, if politicians in charge of NASA’s funding lived in the real planet. That could be a stretch with a Republican-led Household of Reps that experienced trouble electing a speaker—and before this calendar year proposed bludgeoning NASA with a 22 % minimize that would get rid of MSR, stop moon landings and direct to 4,000 layoffs. Perhaps if the community were a lot more vocal, and it were being an election calendar year, Congress may hear. Might.
A monkey wrench in all this is the bipartisan Fiscal Duty Act of 2023, which grew to become regulation in June to thwart the federal federal government defaulting on its financial debt. Element of the fallout from this Act usually means NASA’s finances is capped until ’25. This currently has experienced an effects, as NASA officials are taking into consideration cuts to Hubble House Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, two of the house agency’s workhorse observatories. Rising the spending budget for MSR is effectively impossible as extended as this act is in effect, and the uncertainty in the funding helps make it tough for NASA to know specifically how to transfer ahead on any new layouts.
If MSR—and NASA itself—can weather these setbacks for the subsequent two or three decades, they might nonetheless uncover a route forward. Inspite of all this cacophony, the argument that escalating NASA’s over-all spending plan nevertheless stands. Boosting it by, say, 20 p.c, so to $30 billion for every year, would ease a large quantity of force the company feels when proposing and developing new missions. Even doubling its funding would barely make a dent in countrywide investing, while the payoff would be great. This is not to say that almost everything NASA does is value-helpful I have been vocal about the enormously bloated and decreasingly beneficial Area Launch Method rocket, but its delays and overruns are traceable to congressional meddling in the job. Provided less pork barrel politics and improved management, NASA can provide on its assure: bringing the Universe to Earth.
With MSR we have a genuine shot at investigating some of humanity’s oldest and most fundamental philosophical inquiries. How did we get in this article? Are we by yourself? The value to find these answers, even in the in close proximity to phrase, is rather trifling.
This is an feeling and evaluation posting, and the views expressed by the author or authors are not always these of Scientific American.
[ad_2]
Resource connection