[ad_1]
A mysterious composition nearly 1 billion mild-yrs across has been found in our cosmic community, and it could be a relic from the Major Bang.
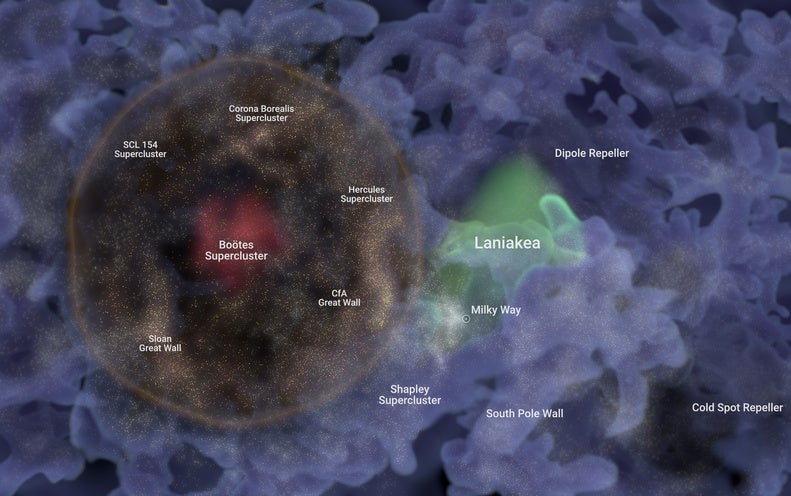
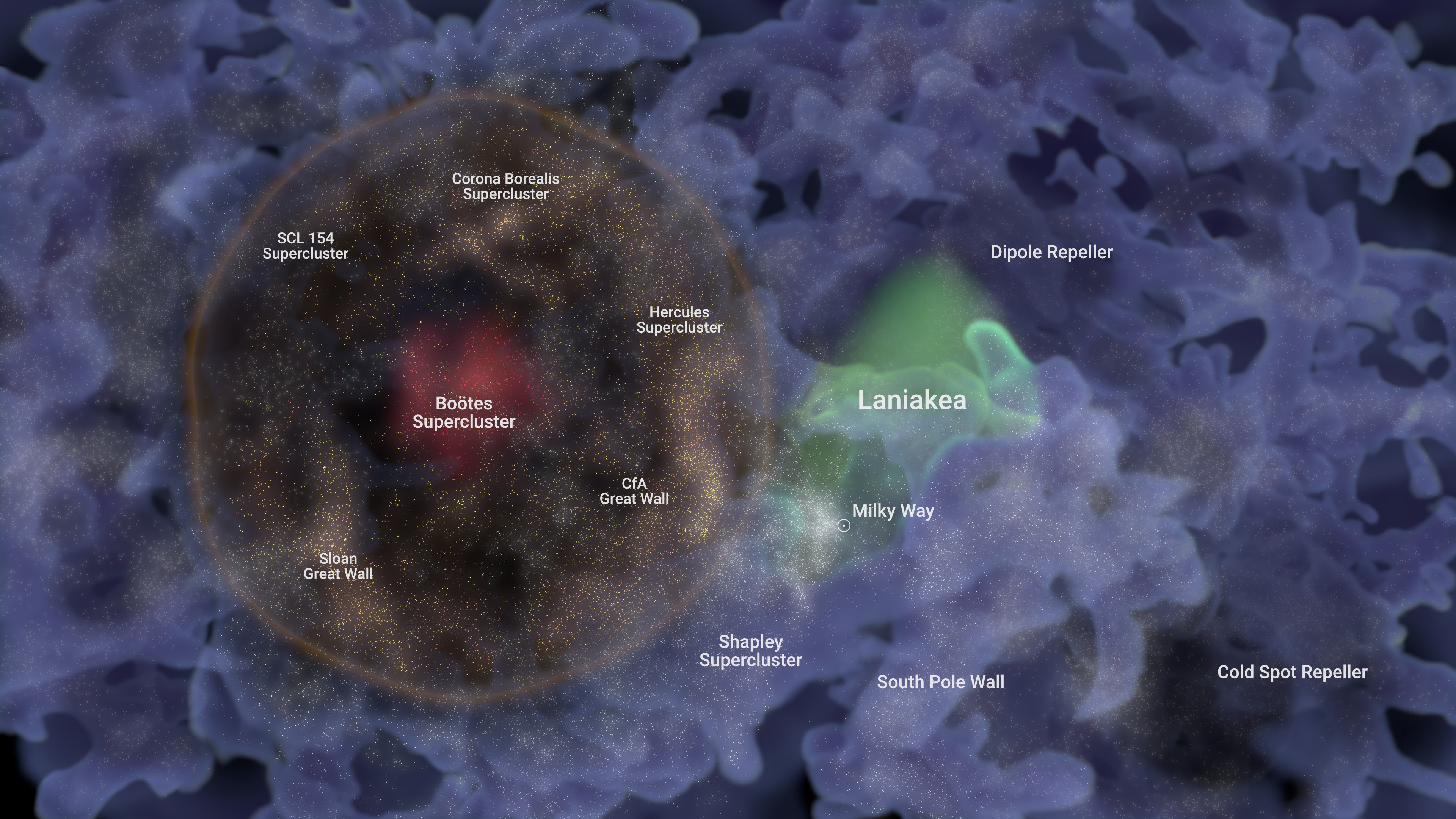
The structure, consisting of a team of galaxies clustered all-around a gigantic spherical void just 820 million mild-several years from the Milky Way, has been named Ho’oleilana, a title encouraged by the Hawaiian development chant, Kumulipo.
It is considered to be a baryon acoustic oscillation, a stress wave frozen in time from the starting of the cosmos and then stretched out to galactic scales by the universe’s growth. The scientists who stumbled upon the bizarre relic posted their results Sept. 5 in The Astrophysical Journal.
“We had been not wanting for it. It is so large that it spills to the edges of the sector of the sky that we were being examining,” Brent Tully, an astronomer at the College of Hawai’i at Manoa, explained in a statement.
Connected: Cosmic file holders: The 12 most significant objects in the universe
The sheer sizing of the bubble defies anticipations and could imply the universe is expanding far more quickly than we believed, Tully stated in the statement.
According to the conventional product of cosmology, the universe started getting condition soon after the Major Bang, when the young cosmos was a roiling plasma broth of matter and antimatter particles that popped into existence only to annihilate each and every other on call. The power of gravity compressed these plasma pockets in on by themselves, squeezing and heating the issue until finally seem waves traveling at 50 % the speed of light — known as baryon acoustic oscillations — rippled outward from the plasma clumps.
These ripples pushed absent the matter that hadn’t currently been drawn into the center of a clump. This outward-flung subject then cooled as a halo all-around the clump. At that position, most of the universe’s subject, slowly congealing into stars and then galaxies, was dispersed as a sequence of slender movies bordering many cosmic voids — like a foamy mass of soap bubbles in a sink.
The astronomers discovered the gigantic void by probability although compiling a catalog of 55,877 galaxies, which they mapped to expose designs in their spacing. From this map emerged a ring 1 billion mild-decades vast, its circumference dotted with galaxies and related to cosmic filaments, and its inside vacant apart from a galaxy supercluster termed the Boötes Supercluster in its center.
“I am the cartographer of the team, and mapping Ho’oleilana in a few dimensions helps us comprehend its written content and partnership with its environment,” Daniel Pomarede, a cosmographer at CEA Paris-Saclay University in France, mentioned in the statement. “It was an amazing procedure to construct this map and see how the giant shell composition of Ho’oleilana is composed of things that were discovered in the earlier as currently being by themselves some of the premier structures of the universe.”
Since Ho’oleilana is even larger than most baryon acoustic oscillations, the scientists think it could be a indication the universe is increasing at a faster amount than very first believed — at approximately 76.9 kilometers for each 2nd for each megaparsec, as opposed to the typical assortment of 67 to 74.
To obtain out if this is true, they say that they will make even a lot more in-depth observations of the petrified cosmic bubble.
Copyright 2023 Stay Science, a Future corporation. All rights reserved. This material may well not be posted, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
[ad_2]
Source link