[ad_1]
7 decades ago an extremely solid El Niño took maintain in the Pacific Ocean, triggering a cascade of harming changes to the world’s weather. Indonesia was plunged into a deep drought that fueled excellent wildfires, although large rains inundated villages and farmers’ fields in components of the Horn of Africa. The party also assisted make 2016 the planet’s hottest year on file.
Now El Niño is back. The odds are good that this a person will be an additional sturdy occasion, increasing considerations of extraordinary temperature in the coming months. And a sturdy El Niño is pretty very likely to established a further world warmth history.
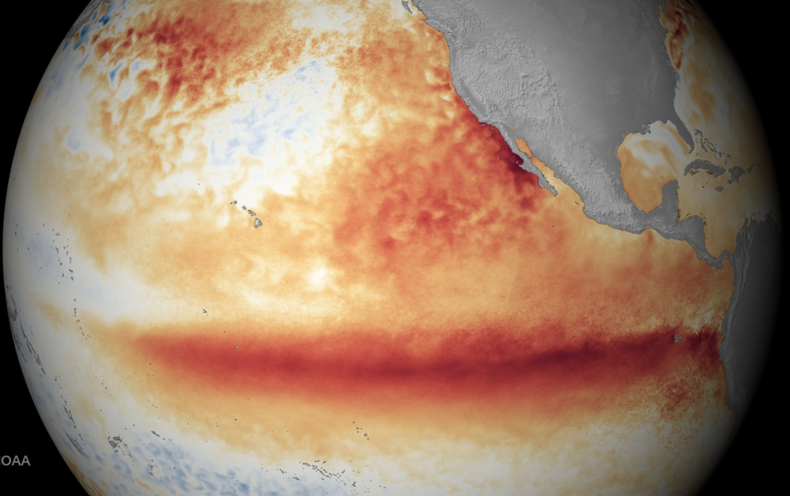
El Niño is component of a pure local weather cycle named the El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Its hallmark is a tongue of hotter-than-standard waters that stretches across the jap and central parts of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Its reverse condition is named La Niña, which capabilities colder-than-ordinary waters in the similar pieces of the Pacific. The ocean seesaws in between these states every two to seven many years, however the previous 3 several years unusually saw 3 again-to-back La Niñas. The improve in ocean surface temperatures in the course of these events alters where warmth is unveiled into the atmosphere overhead. That in convert influences atmospheric circulation designs and sets off a domino outcome that can lead to key alterations to the weather conditions all above the environment.
When and irrespective of whether numerous regions see these improvements is dependent on locale. The closer a area is to the tropical Pacific, the more speedy and likely the results will be. Impacts also are inclined to be additional pronounced when an El Niño reaches its peak toughness, which comes about in the Northern Hemisphere’s winter. “The much better it is, the extra self-confident we are in specified impacts taking place,” suggests Michelle L’Heureux, a forecaster at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Climate Prediction Center. NOAA forecasts a 56 percent probability the existing El Niño will be powerful. (1 of the benchmarks for measuring an El Niño is that temperatures in a particular section of the tropical Pacific are at minimum .5 diploma Celsius, or .9 diploma Fahrenheit, earlier mentioned normal. A sturdy El Niño occurs when all those temperatures are 1.5 levels C, or 2.7 levels F, previously mentioned regular.)
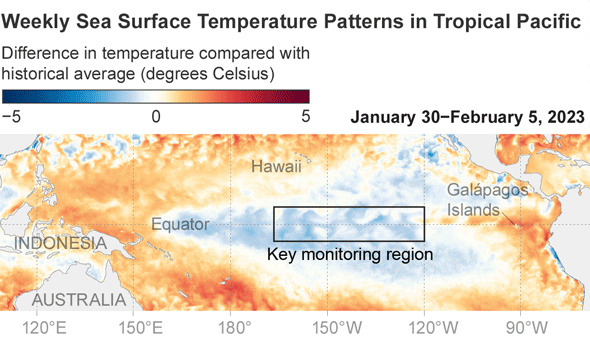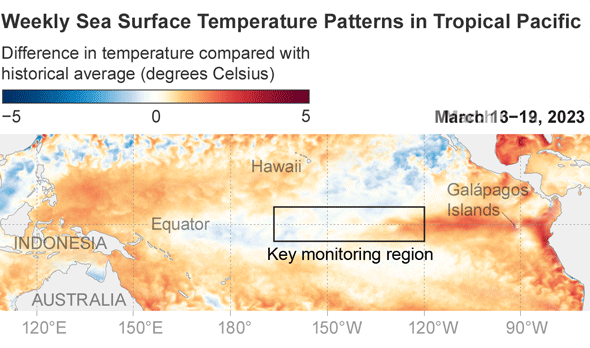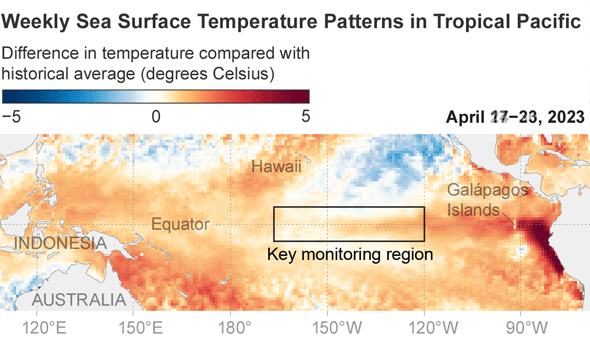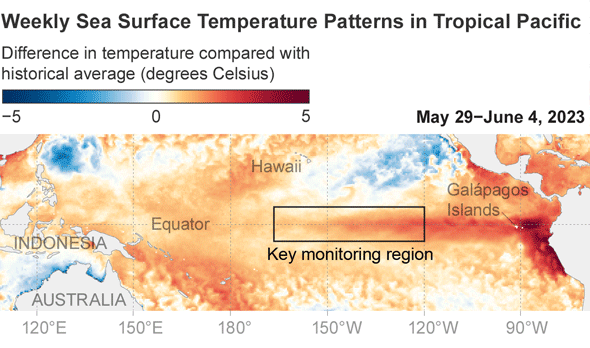 

But even if this El Niño does build into a powerful event—or an very potent one—that’s “not ever a guarantee” that any specific temperature improve will come about, L’Heureux says. Sturdy El Niños frequently provide wet climate to southern California, but that rain did not materialize through the 2016 episode, for case in point. That is simply because El Niño is not the only match in city other all-natural weather cycles and area influences also engage in a position.
The way El Niño variations the world’s temperature is connected to what are referred to as the Walker and Hadley circulations—essentially major vertical loops of air, with the former oriented along the equator and the latter oriented perpendicular to it. Tropical Pacific Ocean waters are generally warmer in the west than in the east. People warm waters fuel convection, with incredibly hot, moisture-laden air increasing and fueling rain until it hits the tropopause, the place the cheapest layer of the atmosphere, the troposphere, meets the stratosphere. The air then flows from west to east, descends about the jap Pacific and subsequently flows from east to west together Earth’s surface area. But throughout an El Niño, anything shifts eastward: air rises around the jap Pacific and subsides in excess of Southeast Asia. This shift qualified prospects to drier climate in the latter region that can lead to major droughts and foods shortages and can gas wildfires.
The shifting Walker circulation also brings descending air to northern South The us and the Caribbean in the course of an El Niño. That subsidence tends to keep a lid on hurricane action in the Atlantic Ocean for the reason that it inhibits the convection that drives these storms. The changing circulation styles also lead to extra crosscutting wind shear, which can stymie storm development. But this year that affect will be competing towards gorgeous, history-breaking very hot temperatures in the Atlantic that will deliver enough gas for storms. With these competing influences, NOAA presently predicts a in close proximity to-ordinary period, with 12 to 17 named storms, 5 to 9 of which could grow to be hurricanes.
U.S. temperature for the duration of an El Niño is also influenced by the Hadley circulation, which runs in a north-south loop on both aspect of the equator. Throughout an El Niño, shifts in that circulation drive the subtropical jet stream—a latest of quickly-going air that guides storm programs throughout the country—farther to the south in the winter months. That commonly qualified prospects to cooler, wetter ailments throughout the southern U.S. and hotter-than-usual ailments across the northern tier of the country and sections of Canada.
Other temperature changes that occur throughout an El Niño involve hotter, drier ailments in japanese Australia, components of India and southern Africa. Pieces of Kenya, Somalia and Ethiopia have a tendency to see greater rainfall, which could be a boon immediately after yrs of local climate-modify-fueled drought. But if much too significantly rain falls much too quickly, it can provide flooding and mudslides and can enable spread waterborne health conditions.
A single of the most significant certainties with an El Niño is that world-wide temperature will ratchet up, as they normally do in the course of El Niño several years, simply because the ocean releases outstanding quantities of warmth into the atmosphere. That heat will be included on to the global warming pushed by humans burning fossil fuels and could spur this yr or upcoming to be the hottest yr on report, as transpired in 2016. (The results on world-wide temperature lag the El Niño by a number of months.) The 2016 El Niño was similar in power to the just one in 1998, but the previous was .5 diploma C (.9 degree F) hotter than the latter for the reason that of global warming. Including to the probability of a report 12 months with the latest El Niño is the truth that the world wide ordinary ocean temperature was now setting data just before the occasion was declared, L’Heureux claims. “That’s rather bonkers,” she adds.
[ad_2]
Supply link