[ad_1]
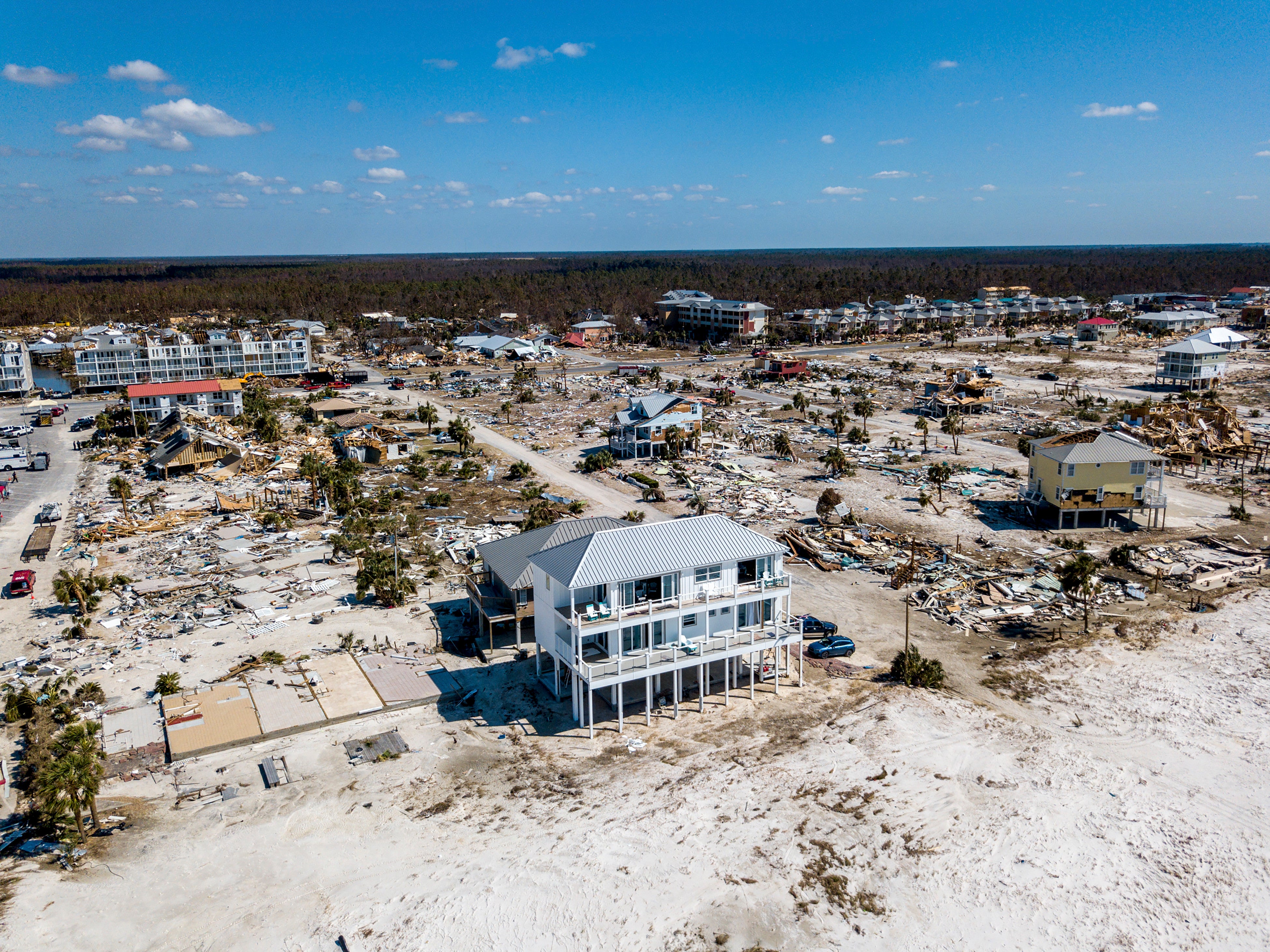

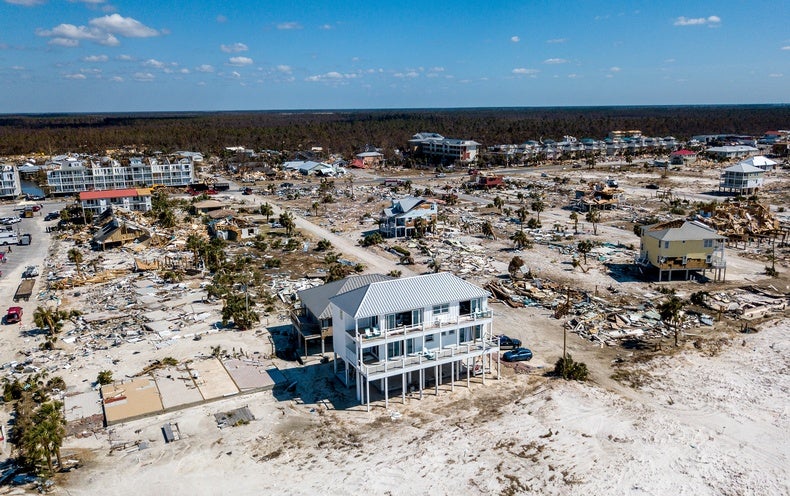
Just after Group 5 Hurricane Michael slammed into Mexico Seaside, Fla., in 2018, there was a dramatic contrast in destruction: properties designed at or over and above state making codes even now stood, whilst a lot of of people developed just before all those stringent codes had been enacted were just gone.
Michael is a single of a increasing selection of multibillion-greenback disasters in the U.S.—the state has already set a document for these disasters so considerably this year—that emphasize how vital constructing codes are to shielding daily life and residence. And as climate alter amplifies hazards, state and nearby governments have to prioritize updating their residential constructing codes to satisfy minimum amount security standards.
These expectations are set, in part, by the Intercontinental Code Council (ICC), an association of creating safety industry experts. Next arduous tests of setting up strategies, surveys executed just after disasters and other analysis, its associates and any intrigued get-togethers function to establish a consensus set of design codes, which are updated every single three yrs. The codes are created to apply to regionally related dangers, from how higher to elevate a property to stay clear of flooding in Louisiana to how much shaking a constructing in San Francisco must be in a position to stand up to. ICC officers convey to us that the strategies they advise can be as simple as employing a particular type of nail or connectors that avert roofs from blowing away in substantial-wind activities.
These suggestions get the job done. A 2018 research in Land Economics found that residences constructed immediately after Florida adopted statewide creating codes based mostly on the ICC’s design codes observed 72 % much less insured losses from wind-associated problems. Each the Federal Crisis Management Agency (FEMA) and the nonprofit National Institute for Building Sciences have located that for each and every $1 put in on conforming to the 2018 ICC code, $11 in problems expenses are saved.
But what making codes develop into legislation in the U.S. relies upon on condition and community governments, ensuing in a bewildering patchwork. A 2020 FEMA review uncovered that 65 % of counties, metropolitan areas and towns throughout the nation have not adopted the most new creating codes and that 30 per cent of new design is occurring in areas that either have no code or have not up to date theirs in 20 many years.
In San Antonio, Tex., for instance, the city has up-to-day codes, but in the unincorporated portion of Bexar County outside the house metropolis limits, county federal government has set no codes in any way. Residents are often unaware that their dwelling may perhaps not be resilient to winds, floods and other dangers, alternatively assuming the governing administration has put right safety specifications in spot.
As Anne Cope, main engineer of the nonprofit Institute for Small business & Home Safety notes, we have basic safety requirements for cribs, but “we have substantial geographic swathes of the United States that have no security standard for the shelter in which that crib is placed.” (You can search up your regional code status at InspecttoProtect.org.)
Homebuilders and policymakers have raised fears that more robust codes would elevate household selling prices. But no study has reliably proven that, and a number of have revealed no effect. Moore, Okla., updated its codes right after a devastating 2011 twister outbreak but did not see an considerable variance in property charges in comparison with close by Norman, which did not enact an up to date code, according to a 2018 analyze. And somewhat compact will increase in up-front prices are recouped by cost savings in insurance policies premiums, electrical power use and averted damage. A sealed roof deck that retains rain out when shingles are blown off might increase to the immediate price of a new house, but it is considerably more affordable than replacing a roof and water-damaged flooring and belongings.
Some officials, notably in smaller jurisdictions, say they deficiency the funding or staff to staff a making code enforcement office environment. Nonetheless there are illustrations of communities in Texas making use of cooperative agreements with more substantial metropolitan areas or, in the scenario of Pompano Seaside, Fla., contracting with personal engineering corporations to triumph over this hurdle.
States ought to also guarantee enforcement by facilitating cooperative agreements and furnishing grants for residences that satisfy specific specifications. Alabama noticed the gain of this kind of grants when property owners who gained them to develop wind-resistant roofs emerged largely unscathed from 2020’s Hurricane Sally. The properties of individuals who did not gain from the grants were included in blue tarps.
The federal government—which has restricted implies to affect building codes—must ramp up initiatives to tie appropriate point out and municipal funding, this kind of as predisaster mitigation grants, to having up-to-day building codes in place. It should really also supply a lot more funding for jurisdictions to satisfy hazard-resistant codes, in addition to electrical power-efficient kinds.
It shouldn’t consider a Hurricane Andrew, a fatal tornado or a devastating flood for authorities officials to make your mind up to adopt a robust creating code. These measures are not just element of climate improve resiliency but very good fiscal organizing and popular perception. The codes should be in position in advance of catastrophe strikes, to avert enormous charges, devastation to communities that are not able to afford to rebuild and quite preventable loss of existence.
[ad_2]
Resource backlink