[ad_1]
Artificial intelligence can style and design an autonomous robotic in 30 seconds flat on a notebook or smartphone.
It’s not quite time to panic about just any person being able to develop the Terminator although waiting at the bus prevent: as noted in a new review, the robots are basic devices that scoot together in straight strains without the need of undertaking more complicated jobs. (Intriguingly, nonetheless, they always appear to produce legs instead than an arrangement that consists of wiggling, relocating like an inch worm or slithering.) But with far more work, the process could democratize robot design, claims review author Sam Kriegman, a computer scientist and engineer at Northwestern College.
“When only massive businesses, governments and large tutorial establishments have sufficient computational electric power [to design with artificial intelligence], it definitely restrictions the variety of the queries currently being asked,” Kriegman states. “Increasing the accessibility of these equipment is one thing which is genuinely exciting.”
AI can now produce essays and drive automobiles, so design may appear to be like a logical next move. But it’s not uncomplicated to produce an algorithm that can proficiently engineer a serious-earth products, claims Hod Lipson, a roboticist at Columbia University, who was not involved in the research. “Many queries keep on being,” Lipson says of the new examine, “but I consider it’s a huge move forward.”
The approach employs a edition of simulated evolution to make robots that can do a precise task—in this circumstance, ahead locomotion. Earlier, making advanced robots concerned producing random variations, testing them, refining the ideal performers with new variations and screening individuals versions yet again. That calls for a whole lot of computing electric power, Kriegman suggests.
He and his colleagues alternatively turned to a technique called gradient descent, which is extra like directed evolution. The method begins with a randomly created physique style and design for the robotic, but it differs from random evolution by offering the algorithm the ability to gauge how well a offered physique plan will accomplish, in contrast with the perfect. For just about every iteration, the AI can home in on the pathways most very likely to guide to success. “We supplied the [algorithm] a way to see if a mutation would be good or lousy,” Kriegman claims.
In their laptop simulations, the scientists commenced their robots as random styles, gave the AI the target of developing terrestrial locomotion and then set the nascent bots free in a virtual natural environment to evolve. It took just 10 simulations and a matter of seconds to get to an ideal condition. From the unique, nonmoving system system, the robots ended up able to start going at up to .5 physique duration for every second, about fifty percent of the ordinary human going for walks velocity, the researchers documented on October 3 in the Proceedings of the Countrywide Academy of Sciences United states of america. The robots also persistently progressed legs and begun going for walks, the team discovered. It was extraordinary that with just a several iterations, the AI could make anything useful from a random type, Lipson suggests.
To see if the simulations worked in exercise, the researchers constructed illustrations of their finest-accomplishing robotic by 3-D printing a mold of the design and filling it with silicone. They pumped air into small voids in the condition to simulate muscle groups contracting and growing. The resulting robots, each about the sizing of a bar of soap, crept along like blocky very little cartoon people.
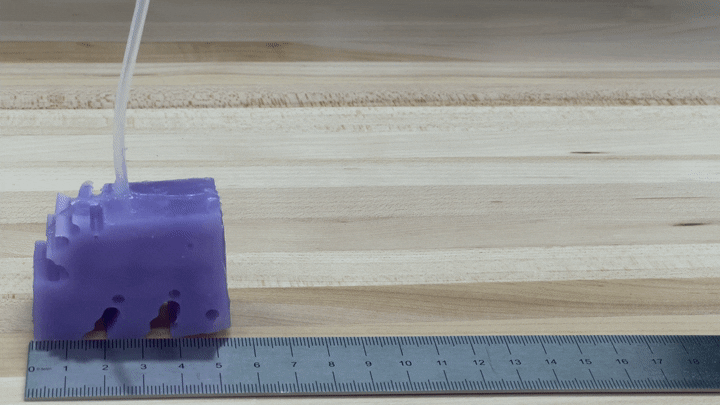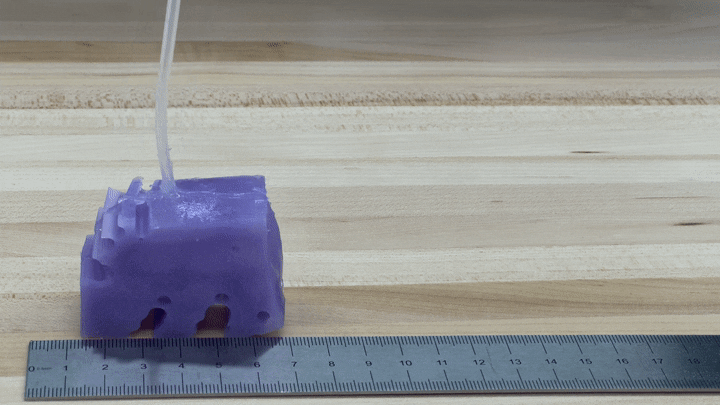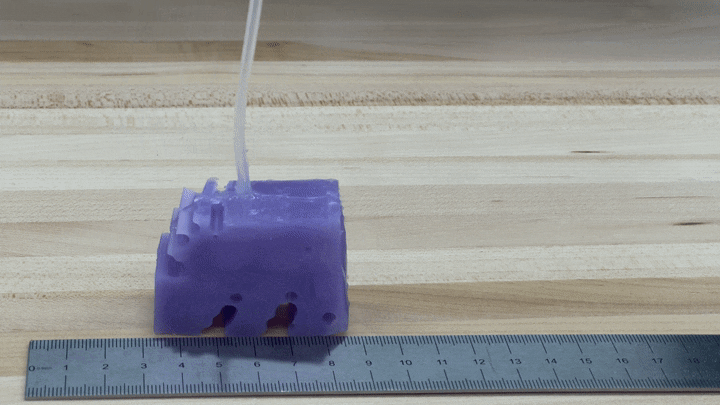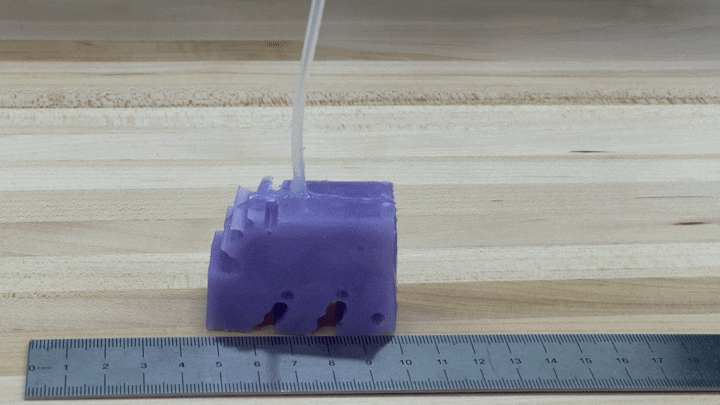 

“We’re genuinely psyched about it just relocating in the appropriate course and moving at all,” Kriegman states, mainly because AI-simulated robots don’t essentially translate into the real entire world.
The investigate signifies a phase towards much more highly developed robotic style and design, even while the robots are pretty easy and can comprehensive only a single process, suggests N. Katherine Hayles, a professor emerita at Duke University and a analysis professor at the College of California, Los Angeles. She is also writer of How We Became Posthuman: Virtual Bodies in Cybernetics, Literature, and Informatics (College of Chicago Push, 1999). The gradient descent method is previously well-set up in developing artificial neural networks, or neural nets—approaches to AI inspired by the human brain—so it would be strong to set brains and bodies jointly, she suggests.
“The actual breakthrough right here, in my opinion, is likely to be when you acquire the gradient descent techniques to evolve neural nets and join them up with an evolvable physique,” Hayles suggests. The two can then coevolve, as comes about in residing organisms.
AI that can structure new merchandise could get humans unstuck from a wide range of pernicious troubles, Lipson states, from creating the up coming-era batteries that could assistance ameliorate local climate modify to finding new antibiotics and remedies for now uncurable illnesses. These uncomplicated, chunky robots are a phase towards this intention, he states.
“If we can design algorithms that can style and design factors for us, all bets are off,” Lipson suggests. “We are heading to encounter an amazing improve.”
[ad_2]
Source website link



