[ad_1]
By Steven Schiff, MD, as told to Stephanie Booth
My patients’ considerations about coronary heart failure are usually, “What is my prognosis?” “What are the therapies, like medication and surgical procedure, that are available to me?” But some men and women will request me for their ejection fraction (EF) range if they’ve study about it, or had it reviewed with them. This is especially correct if they want to know if it is altering in excess of time.
What is EF?
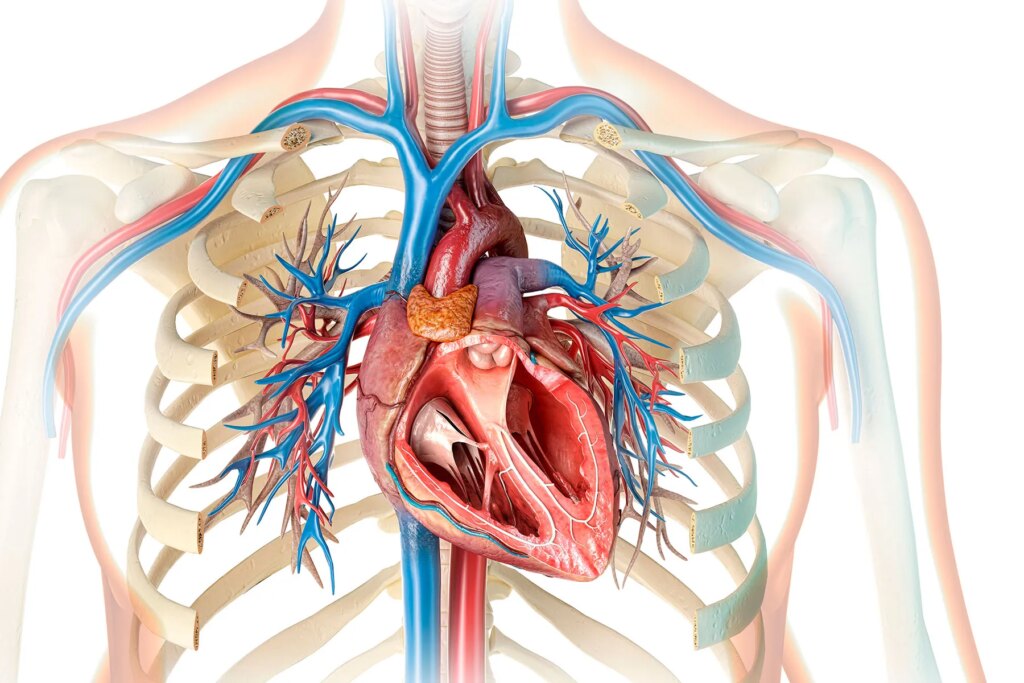
EF is a single of several measurements of how properly your heart performs. It measures the energetic pump functionality of your coronary heart when it contracts and pumps blood out of your coronary heart and into your arteries.
Technically, EF is the share (fraction) of blood that is ejected from your heart as it contracts. (This is also known as the stroke quantity).
Mathematically, EF is the amount of blood pumped with each beat, divided by the amount of money of blood in the chamber when it is filled.
Your coronary heart has two phases for each individual heartbeat:
- A filling phase (diastole)
- A contraction or emptying section (systole)
For that reason, EF is the stroke [contracted] volume/diastolic quantity.
What does EF have to do with heart failure?
A low ejection fraction lets a physician know that the active pumping period of the coronary heart isn’t operating. It truly is generally tied to some, but not all, types of coronary heart failure.
Heart failure with a lower EF is known as “systolic” coronary heart failure.
How is EF calculated?
EF is ordinarily measured, with an echocardiogram or cardiac ultrasound. It can also be calculated for the duration of a heart angiogram and catheterization. That is when catheters (tubes) are place within of you via an artery, into your heart chambers.
Other measurement strategies involve:
- Cardiac MRI
- Cardiac nuclear scans
- Cardiac CT scans
All of these techniques are estimates, and can exhibit slightly distinctive outcomes in the identical particular person.
What do EF quantities signify?
Usual EF is in the assortment of 55% to 70%. As the share falls, it tells the health practitioner that the heart failure is getting worse. In normal, if the EF falls underneath 30%, it’s comparatively intense. A reading of 20% or beneath is pretty serious heart failure.
It’s essential to know that there’s not always a perfect correlation in between indications and the EF. In addition, an EF higher than 75% is deemed also superior, and can be a trouble as nicely.
How can your EF support manage your heart overall health?
Your EF can be a way of assessing the standing and progression of coronary heart failure in excess of time, as well as a way to monitor the advantages of numerous heart failure treatment plans.
For instance, you could be instructed your EF, then commence on treatment or go for surgical procedures, and may possibly want to know: “Did my EF go up or down?” We can keep track of serial measurements of EF (normally by echocardiogram) to see if your treatment is encouraging.
How can you have ordinary EF and coronary heart failure?
Coronary heart failure with a regular EF is going on more and more normally. It can be frequently similar to the filling period of the heart’s cycle of filling and emptying. It is called “diastolic heart failure.”
Normal hearts are quite compliant. This usually means that they fill conveniently, at fairly lower pressures. Sometimes, even though the coronary heart contracts generally (normal EF), it may well want increased force to fill for every beat.
If so, you can have symptoms of heart failure even even though your coronary heart contracts commonly, with a regular EF. You could have fluid accumulation and overload. We see this most routinely in persons with untreated substantial blood strain.
Must you find out your EF?
Most folks with out cardiac troubles do not want to know their EF.
If you are merely anxious about this, ask your medical doctor if you need to be concerned. A very simple echocardiogram will deliver a superior estimate.
The most essential point to know, if you have been instructed of coronary heart failure, is what the underlying bring about is. That will have an effect on your prognosis, therapy, tests and stick to-up.
Amongst the most common will cause [of heart failure] are:
- Coronary artery sickness
- Coronary heart assaults
- Higher blood force
- Coronary heart valve problems
When you’ve been supplied a heart failure diagnosis, you should be seen by a cardiologist for a thorough assessment of your underlying results in, the status of your heart failure, your recent remedy, adhere to up, and prognosis.
[ad_2]
Source link