[ad_1]
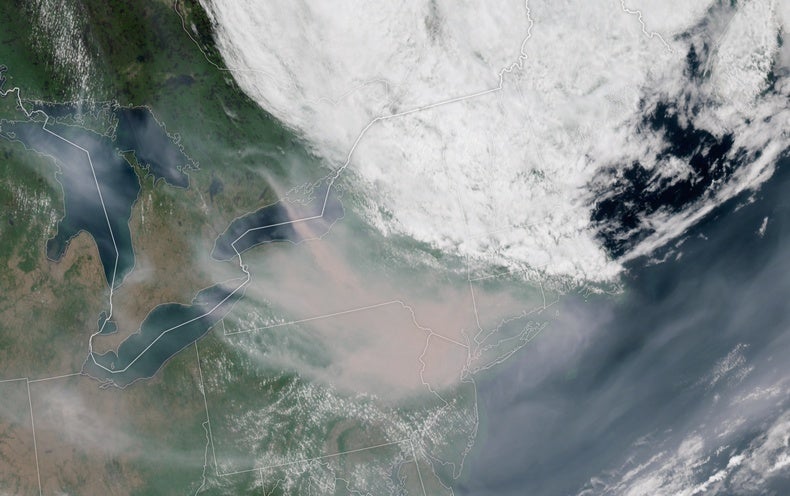
People on the East Coastline earlier this thirty day period skilled something that happens with relative frequency in the West: ominous orange skies lit up by dense wildfire smoke. Throughout the I-95 corridor they responded with many critical concerns: How lousy is the air excellent wherever I live? Can I exercising exterior? When will the smoke go absent?
Lots of Americans, in particular through the wildfire-susceptible West Coast—where climate adjust is creating the infernos worse—are all also acquainted with these questions and seek out responses from smoke-monitoring resources like the AirNow Air Top quality Index. But these tools are only as good as the info that go into them. Presently, the index is primarily based on an extensive community of much more than 1,000 monitors run by point out and area environmental companies.
That may perhaps sound like a great deal, but just about every of these monitors only measures air quality at a single point in space and time. The decrease 48 states span more than 3 million square miles, leaving a lot of air involving screens.
We can and have to do far better.
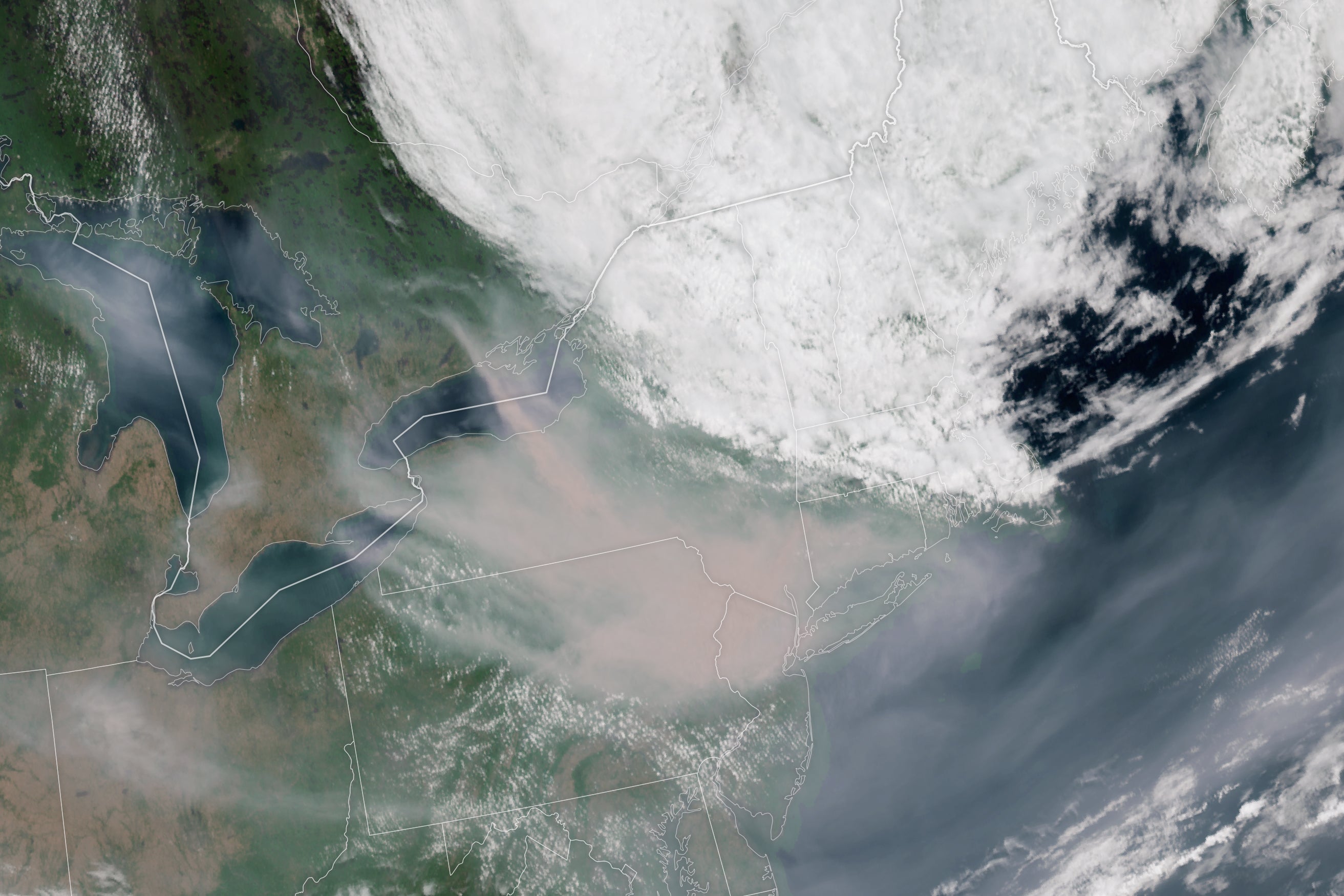
A new technology of place-centered satellites is capturing images of smoke and using measurements of pollution in the Earth’s air with considerably increased coverage than monitors on the floor can regulate. So far, most of these satellites orbit the world when or two times for every day, having a snapshot of each individual site on Earth in the early afternoon at each individual move. This earlier April, NASA released TEMPO, the first air high quality-observing satellite that will continue to be in a preset placement over the U.S. as the world spins, enabling it to consider photos of the Earth’s air for the duration of all daylight hours. TEMPO joins the Geostationary Observational Environmental Satellite, GOES-R, which offers a constant file of temperature, smoke and dust over the U.S. from coastline to coastline. This thirty day period, GOES imagery tracked the Canadian wildfire smoke as it flowed from Quebec to the U.S. East Coastline, pushed by the stagnant minimal-pressure program in excess of Nova Scotia.
Scientists are tough at work combining information from satellites and monitors on the ground to supply applicable and well timed air good quality data almost everywhere across the U.S. Equally of these smoke monitoring instruments are imperfect, but every single contributes precious information to knowing the affect of wildfires on U.S. air high-quality. Ground displays supply direct measurements of dangerous pollutants in smoke plumes at the “nose level” wherever we breathe. Satellites fill in the huge spatial gaps between screens to give air quality facts for everybody throughout the U.S., even these dwelling much absent from a keep an eye on. Satellites also supply vital facts on hearth places and upwind pollution required for forecasting wherever the smoke will go and how negative air pollution ranges will be.
Surveys present that individuals choose action to avoid air pollution exposure through smoke gatherings. At times, this indicates evacuating the polluted location. More frequently, people choose to stay indoors or use a mask to lower their publicity. Just like weather forecasts, air pollution predictions give actionable details to the public. Considering that wildfire smoke is linked with respiratory and cardiovascular disorder, among the other sicknesses, correct and timely smoke forecasts can actually preserve life.
Supplementing floor screens with satellite observations supplies additional in depth details for air excellent alerts, equipping people today with far better facts to protect by themselves. As our research shows, persons getting motion to decrease their publicity during air air pollution gatherings, including all those triggered by wildfires, could prevent approximately 3,000 untimely fatalities nationwide every yr. This is only scratching the floor of the usefulness of air quality info from satellites for shielding general public wellbeing. We have tracked air pollution disparities, air pollution sources and variations in air top quality over time with satellite details, for instance, in our personal investigate.
Despite their enormous value added in filling in the spatial gaps concerning monitors, satellite information data are not guaranteed to keep on. Satellites age, slide into disrepair and are decommissioned about time. The new TEMPO satellite’s main mission is only 20 months extensive. However researchers hope it will retain working for many years past that, satellites should be prepared a long time in progress to make sure that existence-preserving information documents keep on past the missions now in operation.
Luckily, the Countrywide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is setting up a new satellite mission, GeoXO, to get around from TEMPO and deliver hourly air quality measurements throughout the U.S. Inevitably GeoXO is struggling with a gauntlet of complex, political and budgetary decision-making that will identify its foreseeable future. Of course, satellites are pricey. GeoXO’s overall program life cycle cost is $19.6 billion. But our analysis shows that the lessened mortality and illness realized by equipping men and women with superior-high-quality air pollution alerts could be valued at more than $10 billion for each yr. Above the envisioned life span of the satellite, the wellbeing rewards tremendously outweigh the expenses. The overall health savings are also likely to grow as the smoke concentrations we seasoned this thirty day period come to be more widespread under local weather modify.
Substantial-top quality, spatially comprehensive air quality information allows folks defend themselves for the duration of smoke episodes. With the ensuing community health and fitness positive aspects in intellect, GeoXO and other Earth-observing satellites are a deal.
This is an viewpoint and investigation article, and the sights expressed by the writer or authors are not automatically people of Scientific American.
[ad_2]
Resource hyperlink